ABSTRACT
In recent years, significant changes have been made in the internal audit function, based on regulatory stipulations along with the need for improvement of internal audit services. These changes had a significant impact not only on the business itself, but also on the markets and on various stakeholders, and have led to the need to implement a methodology for conducting internal audits based on risk. Our research attempts to record the established status in the Greek shipping companies listed in the New York Stock Exchange NYSE regarding risk based internal audit, based on the perceptions of internal audit professionals. In order to succeed in that, a survey was performed among internal audit employees of various levels at Greek shipping companies listed on the NYSE. The research contains useful conclusions regarding the status of implementation of risk based internal audit methodology. Also, the research focuses on the impact of certain characteristics of internal audit like control activities using multiple regression econometric model based on the regulatory framework for internal audit as provided by the Institute of Internal Auditors. In order to succeed in that, regression analysis was executed based on the results of the aforementioned survey questionnaires. The results revealed significant relationship between risk based internal audit and some the characteristics of internal audit. The conclusion is that risk based internal audit methodology may have viable outcomes to the management of risks within the Greek listed Shipping companies.
Key words: Internal audit, corporate governance, shipping industry, risk based internal audit.
Shipping industry is an essential part of global economy. It is one of the largest sectors in a country's production process, since it links production with consumption. Likewise any transportation facility, shipping transportation is heavily dependent on world production. Greek commercial shipping is an important sector with a very significant impact on the country's economy. Its growth was large and with any kind of assistance by state funding. Its contribution to the national economy has been and continues to be indisputable not only in terms of shipping but also in terms of shipbuilding capital.
Internal control system has been implemented by shipping companies long time ago. However, due to the important changes taking place in the shipping market, internal control system plays a particularly significant role, that of regulatory compliance. Internal audit activity must ensure that the company complies with all relevant regulations (internal and external), by auditing internal control system. In a company with diversified activity, internal audit activity is responsible for auditing key business risks such as risks associated with sales, the costs involved, competition, the wider financial climate as well as the risk of compliance with the institutional framework. In some companies, audit and risk responsibilities have been placed under the Directorate of Internal Control and Risk Management. In such cases, operational risk monitoring is shifting towards the operation of internal control. In addition, the role of the compliance department has been increasing in recent years.
The independence of internal audit activity from the operation of a shipping company has been fully achieved by many shipping companies. One of the most important responsibilities of internal audit within a shipping company is to fulfill its role as an independent assurance provider on the company's Board of Directors. Alzeban (2015) underlines that an auditor has to act independently and that the internal audit activity should have full and unrestricted access to the Board of Directors, whose members should receive periodically internal audit reports. Chief Audit Executive should report functionally to the Board of Directors or the Audit Committee and administratively to Chief Executive Officer. Finally, internal audit activity should audit every activity at its discretion without restriction and free from any influence, that might impair its independence or objectivity. Internal audit staff should also be professional and internal audit activity should comply with the mandatory guidance provided by The Institute of Internal Auditors.
Koutoupis and Tsamis (2009) highlighted the fact that the activity of internal audit of Greek banks is imposed by 2 separate legislations’ sources, the legislation that applies to listed companies and the legislation that applies to Greek banks and comes from the Bank of Greece. According to the above authors, risk based internal audit (RBIA), even though has been evolved as a methodology the past decade, is still not finding application in Greek listed and non-listed companies. Greek banks that included in their research stated that they follow a risk-based audit approach and develop risk based audit plans, but the vast majority of them could not prove it through a clearly documented risk assessment methodology and a risk-based audit plan. However, Bank of Greece has set up some minimum requirements regarding the operation of internal audit functions that are periodically assessed by the aforementioned banking regulator. The research concluded that internal audit and compliance functions should hire high-qualified and competent employees that possess the necessary skills and knowledge to accomplish their duties and responsibilities effectively. The development and adherence to an internal audit manual is also considered essential. Finally, they concluded that Compliance Officers should always evaluate compliance risks in all new products, business practices and types of relationships.
Castanheira et al. (2010) researched the relationship between risk based internal audit and company-specific factors. They investigated the role of internal auditing within the context of enterprise risk management (ERM). Their findings were drawn from a questionnaire survey, sent to all 96 chief internal auditors who were members of the Institute of Portuguese Internal Auditors. They concluded that there is a strong relationship between risk-based annual audit planning and large private entities of financial sector. During planning phase, adoption of a risk-based approach is positive related with the entity size. Velashani et al. (2012) highlighted the close relationship between internal audit and effective and efficient internal control systems. Internal audit provides correct information to management about effectiveness of risk management and internal controls including compliance with organizational laws and regulations. Different techniques of internal audit test the accuracy and the reliability of accounting books and financial reports, the accuracy, reliability and timeliness of control reports and the level of compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. However, in one of these an opinion about qualitative aspects of organizational management, especially risk management, is provided. They provided a comprehensive and practical model for implementing risk-based internal audit methodology. This model was designed based on theoretical principles as well as professional experience of the authors. Coetzee and Lubbe (2013) stated that internal auditing assists with the mitigation of key organizational risks. They concluded that risk management strategy currently implemented by organizations is not mature enough for internal auditing to rely on, and that internal auditing is reluctant to use a pure risk-based approach when performing audit engagements. In particular, internal audit departments still prefer to apply the traditional control-based approach with more emphasis on high-risk areas.
Mihret and Khan (2013) researched theoretically the role of internal audit in the accountability framework within the context of corporate governance. They focused on accountability attribute, in order to conceptualize the risk management rationale of internal audit. In their research, they concluded that the need for accountability within capitalism create the demand for internal audit as a risk management technique that promotes the values of efficiency and effectiveness within firms through the performance of assurance and advisory services. Coetzee (2016), based on the perceptions of chief audit executives (CAEs), the chairs of audit committees and senior management from the South African public sector, concluded that senior management could take advantage of the efforts of CAEs and the chairs of audit committees in order to mitigate key organizational risks. Also, they concluded that audit committee could assess whether internal audit or some other activity contributes to risk management process.
Coetzee and Erasmus (2017) focused on the relationship between effective internal audit function and the improved performance of the public sector, within the South African public sector context. They provided insight into the drivers and measures of internal audit effectiveness. By sending questionnaires to the heads of the internal audit functions, senior management of public institutions and chairpersons of the audit committee and by applying exploratory factor analysis on measures of internal audit effectiveness, it shows that internal audit’s independence is related with five variables, functional reporting, access to information, no scope limitation, access to the audit committee and support by audit committee. Görener (2017) underlined that fundamental changes have taken place in the concept of audit due to several reasons such as accounting scandals, changes in management mentality, technological developments and legal regulations. Along with these changes, risk-based audit approach has been developed beyond the issue of benefiting from the previous period data envisaged by the traditional audit approach.
Zainal (2017) examined the relationship between internal audit, audit committee attributes, risk management and internal control systems with the implementation of risk-based audit, by using data from 117 internal audit functions of public listed companies in Malaysia. The research revealed a positive relationship between “audit committee review and concern” and “risk management system” with the implementation of risk-based audit, while no relationship was found between internal audit experience, size of internal audit function, audit committee qualifications, and internal control system with the implementation of risk-based audit. Rahman et al. (2018), using Islamic banking institutions as a sample, examined whether internal audit is a key function that ensures compliance, taking into account the need to incorporate Shariah audit function to existing corporate governance framework of Islamic banks. Their study provided in-depth explanation on how internal Shariah audit works, especially during the planning phase, the fieldwork phase and reporting phase. Also, they focused on the implementation of risk-based internal audit (RBIA) approach into practice. Klamut (2018) analyzed the effect of internal audit on minimizing the risk of fraud. Research results indicated that internal audit of small firms is implemented sporadically, so it is difficult to talk about its effectiveness, while on other size entities internal audit fulfills its role, provided that is properly carried out. This means that is independent and objective.
Eulerich and Lenz (2019) used as a sample six listed companies and three public/governmental organizations and deployed 26 semi-structured interviews with Chief Audit Executives and internal auditors, in order to analyze the integration of the internal audit function into the organizational governance structure and to identify best practices to improve the overall governance quality, from the perspective of internal audit function. Their results identified different practices of organizing and integrating the internal audit function into the organizational governance. In most of the cases, internal audit function is subordinated to the Board of Directors and therefore has a direct connection to the highest level of management. Koutoupis et al. (2019) examined the relationship between internal audit, corporate governance and the audit committee in the recent financial crisis in Greece and investigated the contribution of internal audit to corporate governance structures during this period in Greece. They concluded that risk based internal audit adds value to the organization and supports senior management towards the accomplishment of the organizational goals.
Marwa et al. (2020) explored the relationship between environmental audit and the quality of environmental disclosures. Using a sample of 81 French non-financial companies listed on the SBF 120 index covering the six-year period from 2012 to 2017, they concluded that a positive relationship exists between the level of voluntary disclosures regarding environmental information and the environmental audit committee, the environmental auditor's BIG 4, debt levels, firm size, earnings management and the industry. Thus, the quality of disclosures of environmental information is an important tool for managers to influence the external perceptions about their company and a strategic tool for managing its legitimacy. Roussy et al. (2020) aimed to understand how internal audit achieves organizational significance. They conducted interviews with audit committee chairs and chief audit executives from multinational corporations. Their findings indicated that internal audit effectiveness achieves and consolidates organizational significance through organizational change.
The purpose of the present study is dual: first, to record the established status in Greek shipping companies listed in NYSE regarding risk based internal audit, based on perceptions of internal audit professionals. Second, the study attempts to explore the interrelation between risk based internal audit and basic elements of the internal audit activity. Our sample consists of the Greek listed shipping companies in New York Stock Exchange, according to NYSE index 2018. More specifically, our sample consists of 25 listed shipping companies. For the first purpose of our study, we conducted a questionnaire-based survey. The questionnaire was sent to all assistants, seniors, managers, senior managers, Executive Directors and Non-executive directors of internal audit departments and audit committees, of the companies of our sample. We received 112 answers out of 150 questionnaires sent (response rate 74.67%). The questionnaire was initially sent on February 2019. The questionnaire was structured containing 6 categories, the first of which was asking general information about the companies and the respondents, and the next five referred to questions related to the variables of the research model under consideration. There were totally 28 questions. The first category of questions consisted of seven questions about gender, years of experience, educational level, position in the company, frequency of internal audits, reasons for performing internal audit and actions taken in case of mistakes and omissions. The other categories consisted of 21 questions presented via the Likert Scale method, where 1 represents “strongly disagree”, 2 “disagree”, 3 “moderate”, 4 “agree” and 5 “strongly agree”.
More specifically the second category is related with dependent variable of our model that is “Risk Based Internal Auditing” and contains 5 questions regarding with internal audit department and code of ethics. The third category refers to dependent variable “Risk Assessment” which includes 5 questions for methodology and control systems. As far as fourth category is concerned it is related with “Control Activities” and contains queries for segregation of duties and limits of approvals. Finally, the fifth and sixth categories concern the role of Internal Audit and the referred to auditors independence and monitoring systems respectively. Based on the literature review presented above, for the second purpose of our research, five variables were selected. The dependent variable was “Risk Based Internal Audit” (RBIA). “Risk Assessment” (RA), “Control Activities” (CA), “Consulting Role of Internal Audit” (ConIA) and “Monitoring Role of Internal Audit” (MonIA) were the independent variables of our model. In order to find the relationship between “Risk Based Internal Audit” and “Risk Assessment”, “Control Activities”, “Consulting Role of Internal Audit” and “Monitoring Role of Internal Audit”, multiple regression econometric models were deployed. The model that we will use in our research is:
RBIA = a + b1RA + b2CA + b3ConIA + b4MonIA + ε
where: RBIA: Risk Based Internal Auditing, RA: Risk Assessment, CA: Control Activities, ConIA: Consulting Role of Internal Audit, MonIA: Monitoring Role of Internal Audit.
General information, regarding gender, years of experience, educational level, position in the company of respondents, frequency of internal audits, reasons for performing internal audit and actions taken in case of mistakes and omissions are presented in Table 1. According to Table 1, the majority of the respondents are men (58%) and most of the respondents work in the same position for more than 10 years (45.5%), 27.7% work from 5 to 10 years and 26.8% work for less than 5 years. This might imply that their opinions regarding risk based internal audit is valid, due to many years of practicing internal audit. Regarding the educational level, the vast majority of the respondents have obtained master degree (66.1%), 22.3% of respondents are university graduates and 8% hold a PhD. Regarding the question about the respondents’ position in the company, most of them 33% are Head of Internal Audit (Executive Directors), 21.4% are members of the Audit Committee (Non-Executive Directors), 16.1% are Senior Internal Auditors, 12.5% are Internal Audit Managers, 10.7% are Assistants and 6.3% are Internal Audit Senior Managers. Regarding the frequency of internal audit, in most of the cases, is performed once a year (87.5%), 8.9% of the respondents replied that internal audit is performed once per two years, and 0.9% replied “once per five years”. Regarding the reasons for performing internal audit, majority of the respondents emphasized on the impact of internal audit in detecting fraud (27.8%) and reviewing the proper operation of procedures (25.9%). 22.3% of the respondents replied that internal audit is useful to identify any errors, or omissions and 18.8% of respondents replied that the reason for performing internal audit is to protect assets. Only 5.4% of the respondents replied that adding value is the reason for performing internal audit. Finally, regarding the reaction in case of mistakes and omissions, 75% of the respondents replied that there are recommendations for corrective actions. Perceptions of respondents regarding the dependent variable of our model, “Risk Based Internal Audit”, are presented in Table 2.
According to Table 2, the most positive responses were given for questions 3 and 4, which are related to the job descriptions carried out at all levels and the clear separation of duties and responsibilities of employees. 42.9% of respondents strongly agree that there is an organization chart for each department, which is reviewed in accordance with current developments and requirements. Half of the respondents also strongly agree that there is a detailed company manual of procedures with imprinted tasks. Finally, vast majority of the respondents agree or strongly agree that a Code of Conduct should be adopted and properly communicated.
Table 3 presents our results regarding “Risk Assessment” independent variable.
According to Table 3, audit procedures are implemented to various extents depending on the risk intensity of the audited Service/ Department (69.6%). Internal control system is applicable not only in regular but also in exceptional cases (51.8%). There are specific targets that are adjusted at regular intervals (42%) and most of the goals set by management are realistic and can be achieved (37.5%). On the other hand, responses about whether there is a specific methodology for assessing the company's risks are quite negative, given that 37.5% disagree and 36.6% strongly disagree with the question.
Table 4 presents our results regarding “Control Activities” independent variable.
According to Table 4, most of the respondents agree (or strongly agree) that the levels and limits of approvals / responsibilities are appropriately communicated (43.8% and 50.9% respectively). Vast majority of the respondents disagree (or strongly disagree) that there is a prior approval of management for the adoption of automated information and other systems of the company. However, they strongly agree that the internal control system protects against unauthorized transactions (66.1%). Finally, the respondents’ answers regarding the statement that job descriptions include specific references to control-related activities are controversial. Table 5 presents our results regarding “Consulting Role of Internal Audit” independent variable. According to Table 5, respondents strongly agree that auditors are providing information to external auditors (79.5%).
Furthermore, auditors are provided with the most reliable information by employees (57.1%). Also, auditors contribute their knowledge to the safe resolution of issues that occur when conducting regular audits in a department of the company or the management (68.8%). Finally respondents disagree (or strongly disagree) that auditors have access to specially designed software to retrieve information from other departments (38.4 and 7.5% respectively). Table 6 presents our results regarding “Monitoring Role of Internal Audit” independent variable.
According to Table 6, vast majority of the respondents disagree (or strongly disagree) that audit activity is evaluated by management of the company (4.8% and 42% respectively). On the other hand, most respondents agree that the departments’ responsibilities are assigned in a way that prevent a person from processing details of a transaction as a whole, executing it, and finally archiving it without further scrutiny by others (52.7%). Finally, respondents neither agree nor disagree that the company has established monitoring systems through budget reporting and other arrangements (60.7%).
As far as the second purpose of our research is concerned, we used SPSS in order to calculate the Pearson correlation matrix for the dependent and independent variables of our model, as well as to perform the actual regression analysis. Results are presented in Tables 7 to 9 accordingly. According to Table 7, we found a significant and positive correlation (r=0.181) between “Risk Based Internal Audit” and “Risk Assessment” at p<0.05 and a significant and positive correlation (r=0.29) between “Risk Based Internal Audit” and “Control Activities” at p<0.05. Also, there is a positive correlation between “Risk Based Internal Audit” and the “Consulting Role of Internal Audit (r=0.135) which is not significant (p>0.05) and there is no significant correlation between “Risk Based Internal Audit” and the “Monitoring Role of Internal Audit (r=0.135, p=0.359).
Moreover, there is a significant and positive correlation (r=0.261) between “Risk Assessment” and “Control Activities” at p<0.05 and a significant and positive correlation (r=0.192) between “Risk Assessment” and the “Consulting Role of Internal Audit” at p<0.05. On the contrary, there is a positive correlation between “Risk Assessment” and the “Monitoring Role of Internal Audit” (r=0.058) which is not significant (p>0.05). Furthermore, there is a positive correlation (r=0.05) between “Control Activities” and the“Consulting Role of Internal Audit” which is not significant (p>0.05) and a slightly negative correlation (r=-0.02) between “Control Activities” and the “Monitoring Role of Internal Audit” which is not significant (p>0.05). Finally, there is a positive correlation (r=0.064) between the “Consulting Role of Internal Audit” and the “Monitoring Role of Internal Audit” which is not significant (p>0.05). Table 8 presents the results of the regression analysis with the application of ANOVA. According to the table, the overall model is significant (F=10.354, sig. =0.002 < 0.05). Finally, Table 9 presents the results of the coefficients of our OLS model.
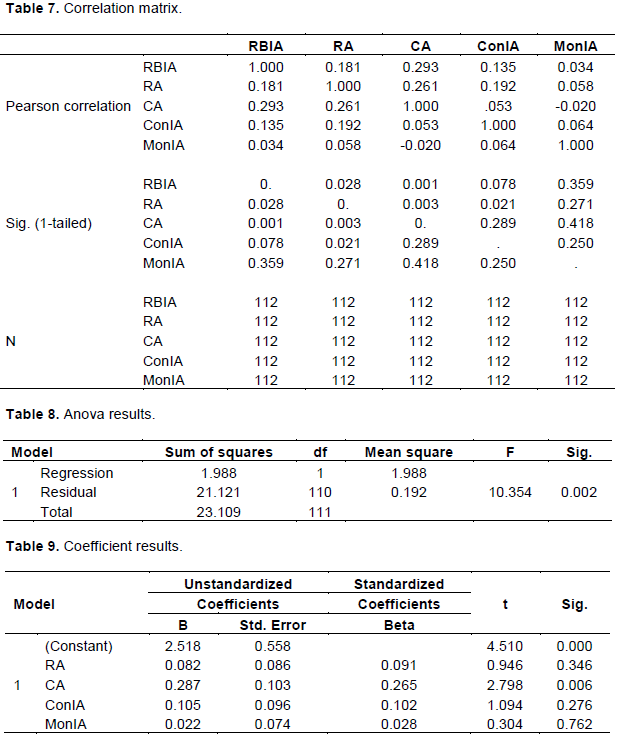
RBIA = a + b1RA + b2CA + b3ConIA + b4MonIA + ε
RBIA = 2.518 + 0.082RA + 0.287CA + 0.105ConIA + 0.022MonIA + ε
The results indicate that there is a positive and significant
relationship between “Risk Based Internal Audit” and “Control Activities” (b2=0.287, p=0.006<0.05). The relationships between “Risk Based Internal Audit” and all other independent variables are positive but insignificant (p>0.05).
Effective management is important for businesses, and one factor that affects it is the implementation of sound corporate governance mechanisms. In a modern and constantly evolving economy, managers take control of businesses, since growth of a company depends on effective management and corporate governance. One of the main pillars of sound corporate governance is the function of internal audit. Internal audit assesses, among others, the effectiveness and the efficiency of the internal control system, which is one of the cornerstones for the achievement of companies’ objectives. In the shipping industry, effective internal control system is a measure of effectiveness of the companies. In Greece, risk management and risk based internal auditing methodology, are at early stages of development, since there is no obligation by the law Greek listed companies to deploy any specific methodology. At academic level, there are many researches regarding risk based internal auditing effectiveness. Our research has concluded that risk based internal audit methodology is essential part for the function of internal audit, as it helps to fulfill its objective of providing reasonable assurance to management through risk management and under the newly established and implemented best practices at international level.
Our research showed that the listed on the New York Stock Exchange Greek shipping companies deploy an organization chart for each Directorate that the division of duties and responsibilities of employees is very clear and that job descriptions have been implemented for all job levels. However, only few of them implement a full risk based internal audit methodology. Their current methodology has not incorporated standardized audit planning procedures. The majority of listed companies use hybrids of methodologies for risk identification and risk management. Moreover, they use a combination of audit processes. A possible explanation might be the lack of specialized knowledge both by board members, managers and internal auditors as well, along with the lack of specific compliance terms at regulatory frameworks. For the second purpose of our research, our results showed that a strong relationship exists between risk based internal audit methodology and risk assessment and control activities, and that also, a relationship exists between risk based internal audit and the consulting role of internal audit. It is worth to mention that, according to our results, both roles of internal audit activity, that of assurance provider and that of the consultant could be supported by the implementation of a risk based methodology.
This study is subject to a limitation related to input data used for the development of our model. In particular, we based our arguments on perceptions of respondents; consequently, a level of bias is embedded. In any case, the fact that we sent our questionnaire only to internal auditors of any level reduces the possibility of existence of bias at respondents’ answers. Another limitation is the conducting of a sector-specific study, which probably restricts the possibility of generalizing our findings. Our research results could be proven useful to Chief Audit Executives, Board members, business executives, consultants, official authorities or any other who express interest for the improvement of internal audit activity and consequently of corporate governance practices in Greece. Future research efforts could be directed to the comparison of our research results with similar researches that used different sample, different time period, and different data regarding risk based internal audit.
The authors have not declared any conflict of interests.
The authors appreciate all the responders and some anonymous reviewers for their comments.
REFERENCES
|
Alzeban A (2015). Influence of audit committees on internal audit conformance with internal audit standards. Managerial Auditing Journal 30(6/7):539-559.
Crossref
Castanheira N, Lima Rodrigues L, Craig R (2010). Factors Associated with the Adoption of Risk-based Internal Auditing. Managerial Auditing Journal 25(1):79-98.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
Coetzee P, Erasmus LJ (2017). What Drives and Measures Public Sector Internal Audit Effectiveness? Dependent and Independent Variables. International Journal of Auditing 21(3):237-248.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Coetzee P (2016). Contribution of Internal Auditing to Risk Management. International Journal of Public Sector Management 29(4):348-364, ISSN: 0951-3558.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Coetzee P, Lubbe D (2013). Improving the Efficiency and Effectiveness of Risk-Based Internal Audit Engagements. International Journal of Auditing 18(2):115-125.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Eulerich M, Lenz R (2019). Internal Auditing's Organization and Relationship to other. Governance Functions, Corporate Ownership and Control 16(4).
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Görener A (2017). Risk Management, Strategic Thinking and Leadership in the Financial Services Industry, in Dincer H., Hacioglou U., (2017). Risk Management, Strategic Thinking and Leadership in the Financial Services Industry (2017). Springer International Publishing AG.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Klamut E (2018). Internal Audit Tool for Minimizing the Risk of Fraud. Financial Internet Quarterly e-Finanse 14(1):49-68.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Koutoupis AG, Pazarskis M, Lazos G, Ploumpis I (2019). Financial Crisis and Corporate Governance: The Role of Internal Audit in the Greek Context. Corporate Board: Role, Duties and Composition 15(2):45-55.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Koutoupis A, Tsamis A (2009). Risk based internal auditing within Greek banks: A case study approach. Journal of Management and Governance 13(1):101-130.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Marwa M, Salhi B, Jarboui A (2020). Environmental Audit and Environmental Disclosure Quality. Scientific Annals of Economics and Business 67(1):1-23.
|
|
|
|
|
Mihret DG, Khan A (2013). The Role of Internal Auditing in Risk Management, Seventh Asia Pacific Interdisciplinary Research in Accounting Conference.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Rahman NA, Mastuki N, Kasim N, Osman MR (2018). Risk Based Internal Shariah Audit Practices in the Islamic Bank. The Journal of Social Sciences Research, Academic Research Publishing Group (5):954-961.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Roussy M, Barbe O, Raimbault S (2020). Internal Audit: From Effectiveness to organizational significance. Managerial Auditing Journal 35(2):322-342.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Velashani B, Jahanbani M, Zafarzade S (2012). Risk Based Internal Audit - An Empirical Model for Implementation. Studia I Materialy, 1-2(14-15):48-58.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Zainal H (2017). Factors influencing the implementation of risk-based auditing. Asian Review of Accounting 25(8):00-00.
Crossref
|
|
|
|