ABSTRACT
The purpose of this study is to provide an insight into the government’s need for sustainable socialization on the importance of paying taxes. This study also aims to analyze the taxpayer's awareness, whether it can mediate the knowledge and understanding of tax regulations on taxpayer compliance or not. The approach in this study is quantitative, with taxpayers as the respondents. The results show that knowledge and understanding of tax regulation and awareness of taxpayers simultaneously contribute to taxpayer compliance. Also, indirectly, knowledge and understanding of tax regulation in the society through the awareness of taxpayer do not have significant influence on tax compliance. Based on the questionnaire, the people have not fully mastered the tax administration using information technology and they have not fully realized the importance of paying taxes for the progress of the nation, due to the different demographic background. This study offers a new understanding and a better perspective of the influence of knowledge, understanding, and awareness of taxpayer compliance. The results will be useful for academics, communities, and governments as they are related to the subject of this study.
Key words: Knowledge and understanding of tax regulation, awareness, taxpayer compliance.
The role of taxpayer awareness and compliance is very important for a nation in an effort to collect the state revenue from tax sector. Why is government attention focused on taxpayer awareness and compliance issues? The answer is, because the understanding and awareness of the people to obediently pay the tax are still relatively low. This is due to the non-optimal tax understanding obtained by the community. Therefore, the people need to be given the understanding of taxes so that their awareness can be developed. This research is based on the problem of unachieved Rural and Urban Land Value Taxes after the delegation of tax management from the central government to local governments, as well as the differences in the results of previous studies concerning the taxpayer compliance. Several studies have explained that: (a) Knowledge and understanding of tax regulation could affect taxpayer compliance, (b) Knowledge and understanding of tax regulation does not affect taxpayer awareness and (c) Knowledge and understanding of taxation can improve the taxpayer compliance through the willingness to pay taxes; the willingness to pay taxes increases due to the taxpayer awareness in which it is influenced by the attitude of the taxpayer itself.
Based on the study of Kariyoto (2010) and Geetha and Sekar (2012), factors that affect the consciousness of taxpayer are described by using the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) developed by Ajzen (1991).Model TPB menjelaskan perilaku kepatuhan memberikan penjelasan yang signifikan, bahwa variabel sikap, norma subyektif dan kontrol keperilakuan yang dipersepsikan berpengaruh terhadap perilaku tidak patuh. The TPB model shows that compliance behavior provides a significant explanation that the variables of attitudes, subjective norms and perceived behavioral controls have an effect on non-compliance behavior.Hasil penelitian berbeda dilakukan oleh Widayati dan Nurlis (2010) menemukan variabel pengetahuan dan pemahaman perpajakan berpengaruh terhadap kepatuhan wajib pajak. Different results are also found in the research of Widayati and Nurlis (2010) where the variables of knowledge and understanding of taxation could affect taxpayer compliance.Hasil ini tidak konsisten dengan peneliti lain yang menemukan hubungan yang positif karena wajib pajak yang sudah memahami peraturan perpajakan kebanyakan berpikir lebih baik membayar pajak daripada kena sanksi pajak. However, these results are inconsistent with that of other researchers who found a positive relationship in their research because taxpayers who already understand the taxation think that it is better to pay taxes than attaining tax sanctions. This study was conducted because of the low level of tax awareness and compliance in Indonesia (Asri, 2004). Assessing the knowledge and understanding of taxation is a variable that can raise people’s awareness to comply with the laws and regulations of taxation. Thus, it is considered necessary to equip the previous research by including the variable, awareness as a mediator of taxation knowledge and understanding towards taxpayer compliance because so far, some researches have explained that: (a) Directly, knowledge and understanding of taxation have influenced awareness, (b) Knowledge and understanding of taxation have direct effect on compliance and, (c) Tax compulsory awareness directly affect willingness to pay taxes and knowledge and understanding of taxation have an indirect effect on compliance through taxpayer awareness.
Rahayu (2010) explained that tax compliance is a condition in which the taxpayer meets all its tax obligations and performs the taxation rights. Kepatuhan menurut Keputusan Menteri Keuangan No.According to the Decree of Minister of Finance number 544/KMK.04/2000 kepatuhan wajib pajak diidentifikasi dari : Tepat waktu menyampaikan SPT untuk semua jenis pajak dalam 2 tahun terakhir, tidak mempunyai tunggakan pajak untuk semua jenis pajak, kecuali telah memperoleh izin untuk mengangsur atau menunda pembayaran pajak.544/KMK.04/2000, taxpayer compliance is identified from the time of submitting tax returns for all taxes in the last two years, having no tax arrears for all types of taxes unless it has legal permission to repay or delay tax payments. The underlying problem of low compliance can be caused by many things but the most important thing here is that there is no data on the taxpayer compliance (Marziana, 2010). Tingkat kepatuhan wajib pajak yang masih rendah akan menimbulkan selisih antara jumlah pajak yang dibayar dengan jumlah pajak yang seharusnya dibayarkan semakin besar. The low taxpayer compliance rate will generate a greater difference between the amount of paid tax and the amount of payable tax; tSelisih tersebut menyebabkan hilangnya penerimaan negara.his difference will cause a loss of the state revenue. The implementation of tax compliance at this time seems to still merely reflect the formal compliance of paying and reporting the tax on time, whereas compliance expected by the government is the material compliance which is filling the Annual Tax Return properly, clearly, and correctly. Kepatuhan formal sudah termasuk kepatuhan material yaitu wajib pajak mematuhi peraturan perundangan dan melaksanakannya. Formal compliance includes material compliance and taxpayers comply and implement the legislation.
Based on this issue, taxpayer compliance has a great role in government revenue; thus, it is necessary to be improved as well as create such obedience culture.Untuk meningkatkan kepatuhan pemerintah telah melakukan sosialisasi, slogan dan poster, mengirimkan surat teguran, imbauan dan surat tagihan pajak. To improve tax compliance, the government has conducted socialization, slogans, posters, warning letters, appeals and tax bills. Bobek dan Hatfield (2003), Mustikasari(2007), Arniati (2009), Widi dan Bambang (2014) dan Imelda (2014) kepatuhan wajib pajak dapat dijelaskan dengan menggunakan
Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) yang dikembangkan Azjen (1991).Bobek and Hatfield (2003),
Mustikasari (2007), Arniati (2009), Widi and Bambang (2014) and Imelda (2014) reported that taxpayer compliance can be explained by using the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) developed by Ajzen (1991). Model TPB menjelaskan perilaku kepatuhan memberikan penjelasan yang signifikan bahwa variabel sikap, norma subyektif, dan kontrol keperilakuan yang dipersepsikan berpengaruh terhadap perilaku tidak patuh wajib pajak orang pribadi.TPB model shows that compliance behavior provides a significant explanation that the variables of attitudes, subjective norms and perceived behavioral controls affect the non-compliant behavior of individual taxpayers. With regards to the importance of taxpayer compliance according Randolph (2015), there are two things that make taxpayers not to be obedient. Pertama, karena ketidaktepatan dalam pembayaran dan/atau pelaporan pajak. First, because of the inaccuracy in payment and/or report.Kedua, ketidaksesuaian jumlah pajak yang dibayarkan oleh wajib pajak karena pengetahuan dan pemahaman peraturan wajib pajak yang minim. Second, the discrepancies in the amount of paid tax due to the low knowledge and understanding of tax regulations.Ketiga, kesadaran wajib pajak yang masih minim tentang arti membayar pajak bagi negara. Third, the minimal awareness of taxpayers with regards to the meaning of paying taxes to the state.
Alabede et al. (2011) believed that consciousness is a will accompanied by action from reflexion to reality. Kesadaran wajib pajak merupakan upaya atau tindakan yang disertai kemauan dan dorongan dari diri sendiri dalam melaksanakan hak dan kewajiban perpajakan sesuai dengan peraturan.Taxpayer awareness is an effort or action accompanied by self-encouragement and willingness to perform the rights and obligations of taxation in accordance with the regulations. Kesadaran wajib pajak dimaknai apabila peraturan perpajakan tersebut telah diketahui, diakui, dihargai dan ditaati. Taxpayer awareness is understood if the taxation regulation has been known, acknowledged, respected and obeyed.Apabila peraturan perpajakan masih sebatas diketahui maka kesadaran wajib pajak masih rendah, rendahnya kesadaran wajib pajak dapat ditenggarai karena rendahnya pengetahuan dan pemahaman peraturan perpajakan dari wajib pajak. If the tax regulation is still limitedly known, then, the taxpayer's awareness is still low. The low awareness of taxpayer is suspected to be caused by the minimum knowledge and understanding of tax regulations. Nugroho and Zulaikha (2012) examined the factors that influence the willingness to pay taxes with the awareness of paying taxes as an intervening variable. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa variabel pengetahuan dan pemahaman akan peraturan perpajakan, pelayanan fiskus yang berkualitas, dan persepsi atas efektivitas perpajakan mempunyai pengaruh signifikan terhadap kesadaran membayar pajakThe results showed that the variables, knowledge and understanding of tax regulations, quality tax services and perceptions of taxation effectiveness have a significant influence on the awareness of paying taxes.
Munari (2005) also explained that taxpayers experience awareness when they: know the existence of laws and provisions of taxation; mengetahui fungsi membayar pajak bagi negara; know the function of paying taxes to the state; memahami hak dan kewajiban yang harus dilaksanakan; understand the rights and obligations to be implemented; mengitung, membayar dan melaporkan dengan sukarela; count, pay and report voluntarily; mengitung, membayar dan melaporkan pajak dengan benar. calculate, pay and report taxes correctly. Based on previous studies, it is deemed necessary to use the awareness variable as one of the variables and studied as a mediation variable.Indikator dari kesadaran wajib pajak diukur dengan mengetahui fungsi pajak, memahami hak dan kewajiban wajib pajak, dapat menghitung pajak, dapat membayar pajak dan dapat melaporkan pajak. The indicators of taxpayer awareness are measured by knowing tax functions, understanding taxpayers' rights and obligations, being able to calculate taxes, being able to pay taxes, and being able to report taxes.
Nugroho and Zulaikha (2012) reported that the knowledge and understanding of taxation regulation is intended for taxpayers so that they can understand the General Provisions and Procedure of Taxation covering the delivery of Annual Tax Return, payment, place of payment, the reporting of Annual Tax Return, fines, as well as the due date of payment and reporting.
Krause (2000) and Santoso (2008) argued that the knowledge or understanding of taxpayers on tax regulation can also affect the obedience of the taxpayer itself. Pendapat Krause ini sejalan dengan OECD (2001) yang menyatakan bahwa pengetahuan wajib pajak akan menentukan tingkat kepatuhan wajib pajak.Krause's (2000) opinion is in line with OECD (2001) which stated that the knowledge of taxpayer will determine the level of taxpayer compliance. Pemahaman ini tidak hanya memberikan pengetahuan namun juga membuat Wajib Pajak mengerti akan hak, kewajiban, dan sanksi apa yang menjadi kewajiban perpajakan, termasuk pada wajib pajak pengusaha orang pribadi (Akintoye and Tashie, 2013)This understanding does not only provide knowledge but also makes the taxpayer understand the rights, obligations and sanctions including the tax of private entrepreneurship (Akintoye and Tashie, 2013).
Theoretically, taxpayer compliance may be influenced by variables such as the knowledge and understanding of taxation regulations (Akintoye and Tashie, 2013; Tan and Fatt, 2007; Behnud and Fahr, 2013) and the taxpayer awareness (Geetha and Sekar, 2012;
Chawla et al., 1996). Dari aspek pengetahuan dan pemahaman peraturan perpajakan, kepatuhan wajib pajak dipengaruhi dari sumber informasi pengetahuan, peraturan perpajakan, hak dan kewajiban wajib pajak ( Larasati, 2013; Alfiah, 2014).From the aspect of knowledge and understanding of tax regulations, taxpayer compliance is influenced by sources of knowledge (information), tax regulations, as well as taxpayer rights and obligations (Larasati, 2013; Alfiah, 2014).
The basic theoretical model to be formed is the interconnection between knowledge and understanding of tax regulation and taxpayer awareness that can improve taxpayer compliance. Kepatuhan wajib pajak dapat dibentuk dari pengetahuan dan pemahaman peraturan perpajakan yang disosialisasikan secara berkelanjutan dari pemerintah kepada wajib pajak. Taxpayer compliance can be built from the knowledge and understanding of tax regulations that are continuously socialized from the government to the taxpayer.Selain itu, kepatuhan wajib pajak dapat ditingkatkan dengan membangkitkan kesadaran wajib pajak melalui kepedulian kondisi suatu negara, mengalokasikan dana, persiapan konsultasi sebelum membayar pajak, mempersiapkan dokumen membayar dan melaporkan pajak. In addition, taxpayer compliance can be enhanced by raising taxpayer awareness through the concern of a country, fund allocation, tax consultation, documents payment preparation and tax report.
This research is conducted within the framework of Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) (Ajzen, 1991) that the determinant of direct behavior is the intention behind the behavior.Niat adalah faktor motivasi yang mempengaruhi perilaku seseorang. Intention itself is a motivating factor that affects a person's behavior. Based on the tax regulations that taxes are coercive and indirect, this received a counter-achievement for taxpayers (Mardiasmo, 2009). Dengan demikian kewajiban pajak harus ditaati oleh semua masyarakat.Thus, the tax obligation must be obeyed by all communities. Jika dilihat dari Kewajiban wajib Pajak bahwa kepatuhan pajak terdiri dari kepatuhan formal dan kepatuhan material, sedangkan kepatuhan pajak dilihat dari niat wajib pajak terdiri dari kepatuhan sukarela dan kepatuhan yang dipaksakan.From the perspective of taxpayer obligation, tax compliance consists of formal compliance and material compliance. While, tax compliance from the intention of the taxpayer consists of voluntary compliance and compulsory compliance.
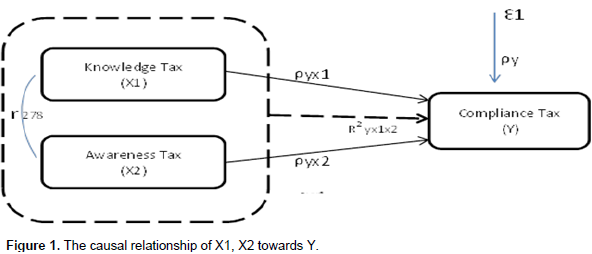
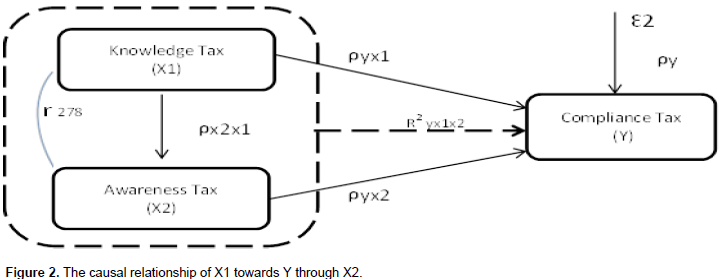
The willingness to pay taxes in order to comply with the legislation is a behavior that is generally given and informed by the attitude of the individual (Kapisillai, 1999). Dengan demikian sikap wajib pajak dalam memenuhi kewajiban perpajakan dimodelkan sebagai berikut (Gambar 1a dan 1b)By that, the attitude of the taxpayer in fulfilling the tax obligation is modeled as shown in Figures 1 and 2. Thus, the hypotheses can be formulated as follows: Hypothesis 1: The knowledge and understanding of tax regulation and taxpayer awareness affected the taxpayer compliance partially and significantly. Hypothesis 2: The knowledge and understanding of tax regulation and taxpayer awareness affected the taxpayer compliance simultaneously and significantly.
To obtain relevant data from taxpayer information, this study combined the method of experiments and surveys by using questionnaires on knowledge and understanding of tax regulations, taxpayer awareness, as well as taxpayer compliance given to respondents as compulsory taxes (Alfiah, 2014; Purnamasari et al., 2015). The questionnaires which were submitted to the respondents consisted of:
1. Request to fill the questionnaire addressed to the taxpayer;
2. The respondent's demographics including name, sex, income, occupation, age, education, and taxation knowledge;
3. Instrument as information measurement tool consisting of knowledge and understanding of tax laws, taxpayer awareness and taxpayer compliance. Responden dimintai untuk menilai instrumen yang disajikan dengan menggunakan skala Likert dengan nilai 1 untuk pernilaian sangat tidak setuju sampai nilai 5 untuk penilaian sangat setuju.
Respondents were asked to rate the instruments presented by using a Likert scale with 1 for a highly disagreeable rate to 5 for a strongly agreed answer. The research population in this study amounts to 1,581,083 with Slovin sample determination together with the level of inaccuracy of 6%. As a result, 278 samples of taxpayers were obtained consisting of the taxpayers of Rural and Urban Land Value Taxes in Malang; the sampling technique was carried out by using a proportional random sampling. The type of book (book I) was chosen with the classification of IDR0,00 – Rp. 0,00 up to IDR200.000,00 dan jenis buku II dengan penggolongan ketetapan Rp.
200,000 and book II by IDR100.000,00 – Rp. 100,000 up to IDR 500.00,00 .500,000. kelompok ini dipilih karena kelompok masyarakat ekonomi klas menengah ke bawah, yang didalam menjalankan kewajiban perpajakan masih dipertanyakan untuk menjalankan kepatuhan pajaknya. This group was chosen because the lower-middle-class community in carrying out the tax obligation is still questionable with regards tax compliance. The data Tanalysis used in this study was path analysis
.Analisis jalur merupakan suatu bentuk penerapan dari regresi berganda yang menggunakan diagram jalur sebagai petunjuk terhadap pengujian hipotesis yang komplek. Path analysis is a form of multiple regression application by using path diagrams as an indication of complex hypothesis testing.Analisis jalur ini dapat dilakukan untuk mengestimasi besarnya pengaruh baik langsung maupun tidak langsung. Analysis of this path can be done to estimate the magnitude of the effect either directly or indirectly.
Based on Table 1, substructural 1 is about the relationship structure of knowledge and understanding of tax regulation (X1), taxpayer awareness (X2) and taxpayer compliance (Y). Simultaneously, knowledge and understanding of tax regulation and taxpayer awareness affect the taxpayer compliance by 0.779 or 779%; while 0.221 or 22.1% is influenced by other factors outside the model. Pengaruh secara langsung pengetahuan dan pemahaman peraturan perpajakan berpengaruh positif dan signifikan terhadap kepatuhan wajib pajak yang ditunjukkan oleh koefisien jalur sebesar 1,022 , pengaruh individual pengetahuan dan pemahaman peraturan perpajakan terhadap kepatuhan wajib pajak ditunjukkan t hitung sebesar 17,998 dengan signifikansi (ρ) 0,0000 < 0,05 maka berdasarkan hipotesis I : dapat diterima pengaruh pengetahuan dan pemahaman peraturan perpajakan berkontribusi dan signifikan terhadap kepatuhan wajib pajak.The direct influence of knowledge and understanding of tax regulation has positive and significant effect on taxpayer compliance shown by path coefficient as much as 1,022, while the influence of individual knowledge and understanding of taxation on taxpayer compliance is shown by t-count which is equal to 17.998 with the significance of (ρ) 0.0000<0.05. Then, hypothesis 1 is acceptable that the influence of knowledge and understanding of tax regulation significantly contributes to taxpayer compliance.Pengaruh secara langsung kesadaran wajib pajak berpengaruh negatif dan signifikan terhadap kepatuhan wajib pajak yang ditunjukkan oleh koefisien jalur sebesar -0,166 atau sebesar -16,6% pengaruh individual kesadaran wajib pajak terhadap kepatuhan wajib pajak ditunjukkan t hitung sebesar -2,927 dengan signifikansi (ρ) 0,0,400 < 0,05, maka berdasarkan hipotesis II : dapat diterima pengaruh kesadaran wajib pajak berkontribusi negarif dan signifikan terhadap kepatuhan wajib pajak. The direct influence of taxpayer awareness has a negative and significant effect on taxpayer compliance and is shown by the path coefficient (-0.166) or equal to -16.6%; the influence of taxpayer awareness on taxpayer compliance is shown by t-count that is -2.927 with the significance of (ρ) 0.0400<0.05. With that, based on hypothesis II, it is acceptable that the influence of taxpayer awareness has a negative and significant effect on taxpayer compliance. As shown in Table 1, substructural 2 is in accordance with the relationship structures of knowledge and understanding of tax regulation (X1) on the taxpayer awareness (X2). The path coefficient is 0.866 or 86.6% with the remaining 13.4% influenced by other factors outside the model.Sedangkan pengaruh langsung pengetahuan dan pemahaman peraturan perpajakan terhadap kedasaran wajib pajak ditunjukkan t hitung sebesar 28,810 dengan tingkat signifikasni (ρ) 0,0000 < 0,04, maka berdasarkan hipotesis II: dapat diterima pengaruh pengetahuan dan pemahaman peraturan perpajakan terdapat kesadaran wajib pajak. The direct influence of knowledge and understanding of tax regulation on taxpayer awareness is shown by t-count of 28.810 with the significance level of (ρ) 0.0000<0.04. As a result, hypothesis II is acceptable and there is a relationship between knowledge and understanding of tax regulation and taxpayer awareness.
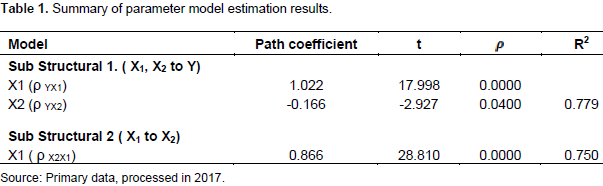
Table 2 shows the value of F which is equal to 483.313 with the probability of (ρ) = 0.0000<0.05. Then, it can be said that hypothesis II is accepted; the knowledge and understanding of tax regulation and taxpayer awareness have an influence on taxpayer compliance, therefore, the partial (individual) test can be done. In the partial test (individual), the path coefficient is 1.022 which indicates the direct influence of knowledge and understanding of tax regulation on tax compliance with t-count by 17.998 and probability (sig) by 0.0000. The value of α < 0.05, makes H0 to be rejected and Ha accepted which means that the path coefficient is significant. So, it can be said that the knowledge and understanding of tax regulation have contributed significantly to taxpayer compliance. Moreover, direct testing can be described as shown in Figure 3.The analysis of X1 for Y: fDfrom the above analysis, the significance value of X1 was 0.0000<0.05, so that there is a significant effect on X1 for Y. The analysis of X2 for Y: the significance value of X2 is 0.004<0.05. Thus, it can be concluded that X2 is significantly affected by Y.
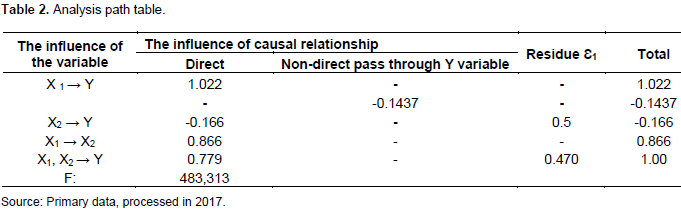
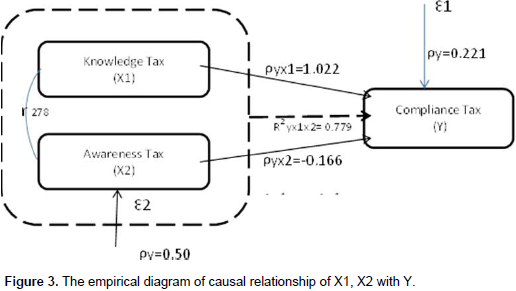
Taxpayer awareness testing as an intervening variable in the relationship of knowledge and understanding of tax regulation towards taxpayer compliance
The analysis of X1 through X2 to Y is known as the direct influence of X1 to X2 is 0.866, while the indirect influence of X1 to X2 on Y is -0.1437 obtained as 0.866 x -0.166. The total effect is generated from the sum of direct effect and indirect effect: 0.866 + (-0.1437) = 0.7223. Based on the calculation, the value of the direct effect is 1.022 and indirect effect is -0.1437 which means that the direct effect is greater than the indirect effect. The results show that, indirectly, X1 through X2 to Y does not have a significant influence on Y (Figure 4).
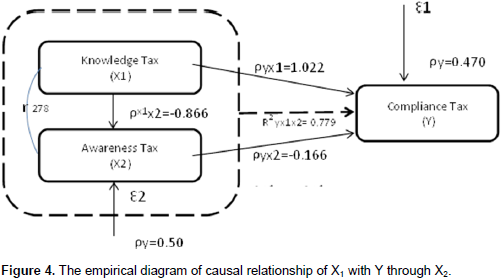
Model accuracy
The accuracy of the hypothesis model in this research is measured by the relationship of coefficient determinant R2 in both equations.Pengujuan petepatan model diperlukan untuk menentukan apakan model yang diajukan ssudah seuai (fit) tau konsisten dengan data. The test of model accuracy is necessary to be implemented to determine whether or not the model proposed is appropriate or consistent with the data. Penyjian model dilakukan dengan membandingkan matrik korelasi teoritis dan matrik korelasi empirisnya.The model is presented by comparing the matrix theoretical correlation and matrix empirical correlation. Jika kedua matrik tersebut telah sesuai, maka model teoritis yang diajukan dapat diterima secara sempurna.If both matrices are appropriate, then the proposed theoretical model is perfectly acceptable.
R2 Model = 1-(1-R21) (1-R22)
= 1-(1-0.779)(1-0750)
= 1-(0.221)(0.250)
= 1-(0.05525)
= 0.9447 or 94.47%
Based on the test results above, the value of 0.9447 or 94.47% points out that the model contribution could explain the relationship of the three variables studied
The hypothesis test shows that knowledge and understanding of taxation in the society is already good, meaning that higher knowledge and understanding of taxation regulation will create higher compliance in carrying out the taxation obligation. In contrast, lower knowledge and understanding of taxation regulation will decrease the compliance of taxation.Temuan penelitian ini sesuai dengan apa yang dilakukan Rahman Adi Nugroho (2012) dan Munari (2005) kelas ekonomi suatu masyarakat, misalnya akan semakin menentukan siapa yang akan memperoleh seberapa banyak dan ragam informasi pengetahuan perpajakan beserta semua konsekuensi yang ditimbulkannya. The findings of this study are in accordance with the research of Nugroho and Zulaikha (2012) and Munari (2005), discussing an economic class of a society; for example, this will increasingly determine who will get much and various information of taxation knowledge and all the consequences in the society.Didalam keadaan seperti ini masyarakat ditunjukkan pilihan pembayaran pajak tepat waktu untuk menghindari denda dan membayar pajak adalah salah satu bentuk kepeduliaan masyarakat terhadap pentingnya membayar pajak bagi negara untuk pembangunan bangsi dn negara. In such circumstances, the public is given the option to pay taxes on time in order to avoid fines and it is one form of public awareness of the importance of paying taxes for the construction of the nation. This study proves that the contribution of knowledge and understanding of tax regulation leads to a better compliance in the society.
Dengan meningkatnya pengetahuan dan pemahaman peraturan perpajakan membuktikan paling berpengaruh terhadap kepatuhan pajak karena dasar pemungutan pajak adalah Undang-undang yang dapat dipaksakan.The most influential aspect of tax compliance is the increased knowledge and understanding of tax regulation because tax collection is based on a law that can be imposed. Dengan Undang-undang dan peraturan perpajakan khususnya pengenaan sanksi dapat menambah meningkatkan kepatuhan wajib pajak dalam melaksanakan kewajiban perpajakannya. With the laws andregulations of taxation, especially the imposition of sanctions, this can increase taxpayer compliance in carrying out its tax obligation. Temuan ini bertentangan dengan hasil penelitian Bernadette K, Christian K dan Erich Kirchler (2010) yang menyimpulkan kurangnya pengetahuan dan pemahaman perpajakan pemilik usaha kecil cenderung tidak mematuhi membayar pajak. On the other hand, these findings are contradictory to the findings of Bernadette et al. (2010) who concluded on the lack of knowledge and understanding of taxation by small business owners who are less likely to comply with the tax payment.Hasil penelitian ini mendukung penelitian dari Machogu dan Jairus (2013); Nevertheless, the results of this study support the research of Machogu and Amayi (2013), Mas’ut (2004), Laksono and Ardiyanto (2007), Kariyoto (2010), Pratama (2012) and Sjursen et al. (2014) who agreed that there is an influence of tax knowledge and understanding on the compliance in carrying out tax obligations.Krause (2000) dalam Wahyu Santoso (2008) berpendapat bahwa semakin banyak mayarakat yang memahami peraturan perpajakan maka target penerimaan negara dari sektor pajak dapat terpenuhi, karena masyarakat menyadari arti penting pajak bagi negara. Krause (2000) and Santoso (2008) argued that the more, people understand the tax laws, the higher the state revenue obtained from the tax sector because the public realizes the importance of taxes to the state.This study proves the awareness of taxpayers in making tax payments and reports has demonstrated the formal compliance that is, making tax payments and reports right on time. Pengetahuan dan pemahaman peraturan perpajakan yang dimiliki wajib pajak selain memberikan pemahaman hak dan kewajiban wajib pajak, manfaat membayar pajak bagi negara dan khususnya dalam melakukan pembayaran Pajak Bumi dan Bangunan, maka manfaatnya lebih banyak kembali pada pengembangan dan pembangunan wilayahnya, karena Pajak Bumi dan Pangunan merupakan pajak lokal. Knowledge and understanding of taxation regulation by the taxpayer not only gives an understanding of taxpayer's rights and obligation, and the importance of paying taxes to the state especially in making payment of Land and Building Tax, but also benefits regional development because Land and Building Tax is actually a local tax.
From the research, it can be concluded that: Firstly, the knowledge and understanding of tax regulation in the society will increase if the government conduct more socialization about the regulation and legislation of taxation and its amendments. Secondly, the research proves that the knowledge and understanding of tax regulation and taxpayer awareness has a significant direct effect on tax compliance, both individually and simultaneously.
Finally, it was also found that the direct effect of knowledge and understanding of tax regulation on tax compliance is greater than the indirect effect. This implies that the knowledge and understanding of tax regulation through taxpayer awareness does not have a significant influence on tax compliance.
The results of the research suggests that the Board of Regional State Revenue is expected to increase the quantity of taxation socialization to the community continuously or periodically in order to provide such additional knowledge and understanding of tax regulations, as well as to improve the service quality in terms of the facility to provide satisfaction to the taxpayer.
The authors have not declared any conflict of interests.
The authors thank the Directorate of Research and Community Service (DRPM) for funding this research. This research is part of a dissertation.
REFERENCES
|
Ajzen I (1991). The Theory of Planned Behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 50:179-211.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
Akintoye IR, Tashie GA (2013). The effect of tax compliance in economic growth and development in Nigeria. British J. Art Social Sci. UK 11:2.
|
|
|
|
|
Alabede OJ, Ariffin ZZ, Kamil MI (2011). individual taxpayers' attitutes and compliance behaviour in Nigeria: The moderating role of financial condition and risk preference. J. Account. Taxat 3(5):91-104.
|
|
|
|
|
Alfiah I (2014). Awareness of Taxation, Tax Penalties, attitude of tax authorities, the Environment Taxes, Tax Regulations Knowledge, Perceived Effectiveness Tax System, Willingness to Pay Taxes Against Individual Taxpayer Compliance. e-Jurnal Accounting University Muria Kudus.
View
|
|
|
|
|
Arniati L (2009). Peran Theory of Planned Behavior terhadap Ketaatan Wajib Pajak. In Seminar Nasional Perpajakan II. Universitas Trunojoyo Madura.
|
|
|
|
|
Behnud MD, Fahr R (2013). The Effect of Tax Knowledge and Budget Spending Influence on Tax Compliance. IZA Discussion Paper No. 7255, University of Paderborn, Germany.
|
|
|
|
|
Bernadette et al. (2010). Tax compliance of small business owners)", Int. J. Entrepr. Beh. Res. 18:330-331
|
|
|
|
|
Bobek D, Hatfield RC (2003). An investigation of theory of planned behavior and the role of moral obligation in tax compliance. Behav. Res. Account. 15:14-38.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Chawla M, Govindaraj R, Berman P, Needleman J (1996). Improving Hospital Performance through Policies to Increase Hospital Autonomy: Methodological Issues. USAID. Washington 15:13-38.
|
|
|
|
|
Geetha R, Sekar M (2012). E-Filing of Income Tax: Awareness and Satisfaction level of individual Tax payers in Coimbatore city, India. Res. J. Manage. Sci. 1(4):6-11.
|
|
|
|
|
Asri HA (2004). New Paradigm Indonesian Taxation Perspective Economy-Politics. Jakarta. Integrita Dinamika Press. pp.114-118
|
|
|
|
|
Imelda B (2014). Analysis of factors affecting tax compliance private person. Skripsi.Universitas Diponegoro. Semarang. 12(1).
|
|
|
|
|
Kasipillai, Jeyapalan et al (1999). Are Malaysian Taxpayers Prepared for the Self Assessment System?' September Tax Nasional 9. 1999
|
|
|
|
|
Kariyoto (2010). Effect of tax reform, tax audit, awareness and compliance taxpayers against taxation performance. Unpublished Dissertation.Brawijaya University.
|
|
|
|
|
Krause TR (2000). The Behavior-Based Safety Process. Willeys Publisher. Second Edition. New York.
View
|
|
|
|
|
Laksono JP, Ardiyanto MD (2007). Analysis of Factors Affecting Taxpayer Compliance in Manufacturing Industrial Company in Semarang. 4(8).
|
|
|
|
|
Larasati LD (2013). Influence Perception of sanctions Taxation Taxpayer Awareness and Characteristics of the Compliance Reporting taxpayer individual taxpayer. Essay. Muhammadiyah University. Surakarta. JEP:KMEP. Printed ISSN: 1411-6081. Vol. 14(1).
|
|
|
|
|
Machogu CG, Amayi JB (2013). The effect of taxpayer education on voluntary tax compliance, among SMES in Mwanza City – Tanzania. Int. J. Market. Financ. Serv. Manage. Res. 2:8.
|
|
|
|
|
Mardiasmo P (2009). Taxation. Publisher Andi. Yogyakarta. pp. 21-23.
|
|
|
|
|
Pratama MR (2012). Analysis of Factors Affecting Awareness of Individual Taxpayers Against Compliance Tax Obligation In South Tangerang City. Thesis. University of Bina Nusantara, Jakarta.
|
|
|
|
|
Marziana BHM (2010). The relationship between perception and level of compliance under self assesment system - A study in the East Coast Region. J. Glob. Bus. Econ. pp. 241-257.
|
|
|
|
|
Munari A (2005). Influence success factors against tax payer acceptance of income tax (KPP Case Study Batu, Malang). Executive J. 2(2):120-124.
|
|
|
|
|
Mustikasari E (2007). Empirical Study of Taxpayer Compliance in Processing Industry Company in Surabaya. The Tenth National Seminar in Accounting. Macassar. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) (2001). OECD Profuctivity Manual : A Guide to the Measurement of Industry Level and Aggregate Productivity Growth OECD. Statistics Directorate for Science, Tecknology and Industry. Paris. Maret 2001
|
|
|
|
|
Purnamasari YA, Hamid D, Susilo H (2015). The influence of service quality of integrated service place official and taxpayer comprehension of taxpayer compliance. J. Tax. 1:1.
|
|
|
|
|
Pratama MR (2012). Analisis Faktor – Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Kesadaran Wajib Pajak Orang Pribadi Terhadap Kepatuhan Kewajiban Perpajakan Di Kota Tangerang Selatan. Thesis. Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta.
|
|
|
|
|
Rahayu SK (2010): Indonesian Taxation - Concepts and Formal. Yogyakarta: Graha Science. pp. 56-71.
|
|
|
|
|
Randolph NA (2015). Influence of individual ethical orientation on tax compliance: Evidence among Ghanaian Taxpayers. J. Account. Tax. 7(6):98-105.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Santoso W (2008). Failure risk analysis as the basis for increased taxpayer taxpayer compliance. J. Publ. Financ. .5 (1):85-137.
|
|
|
|
|
Sjursen IH, Ali N, Odd-Helge F (2014). To pay or not to pay, citizents, attitudes toward taxation in Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, and South Africa. World Dev. 64: 828-842. 0305-750X/2014, Elsevier Ltd.
|
|
|
|
|
Tan ML, Fatt CC (2007). The Impact of Tax Knowledge on the Perceptions of Tax Fairness and Attitudes Towards Compliance. Asian Rev. Account. 7 (1):44-58.
|
|
|
|
|
Widayati dan Nurlis (2010). Factors affecting willingness to pay taxes, tax payer an individual that did the job free (A Case Study Three Gambir STO). National Symposium Papers Accounting XIII.Purwokerto.
|
|
|
|
|
Zulaikha, Nugroho RA (2012). Willingness to pay taxes, pay taxes awareness, knowledge and understanding of taxpayers, a good perception of the effectiveness of the taxation system, service quality. Dipenegoro J. Account. 1:2.
|
|