This study examined administrative challenges and principals’ managerial effectiveness in Ogun State secondary schools. The study population was 13,123 teachers in the state’s secondary schools from which a sample of 900 teachers was drawn from 35 schools using simple random and proportionate random sampling techniques. A self-developed instrument tagged Administrative Challenges and Principals’ Managerial Effectiveness Questionnaire (ACPMEQ) was used to gather information from the respondents. The instrument was validated with a reliability coefficient of 0.78. The hypotheses were tested using Pearson’s Product Moment Correlation at 0.05 level of significance and the outcome revealed that a significant relationship exist between administrative challenges and principals’ managerial effectiveness as well as well-equipped school libraries and managerial effectiveness of principals. However, there was no significant relationship between incessant teachers’ transfer and principals’ managerial effectiveness. It was equally revealed from the study that finance is the best predictor of principals’ managerial effectiveness while physical facility is the least predictor. Based on the findings, it was concluded that administrative challenges are critical variables of principals’ managerial effectiveness. It was therefore recommended that government should give out its supportive arms by releasing grants to schools as and when due and also allow them to collect meager sum of money either on termly or yearly basis which should solely be spent on developmental projects. It was also recommended that within the limited resources available to schools, principals should endeavour to stock the libraries with necessary textbooks.
Education has been the bedrock of development all over the world and it is believed that the way out of the series of problems plaguing nations and individuals is through education. Education in all countries of the world has been considered very important for personal and societal development. Thus, the educational standard set up for schools must be challenging in order to meet the needs of the students and the society (Adekoya et al., 2008). Secondary education does not only occupy an important place in the Nigerian education system, it also serves as a link between the primary and tertiary levels; and because of its central position, its programmes have functional roles such as giving students access to higher education as well as preparing them for work. Enose (2010) summed it up that educational organization such as the secondary school system exist in a symbiotic relationship with its environment, while utilizing both human and material resources for the production of educated socialized graduates. The principal as school leader occupies a unique and strategic position in the secondary school administrative structure since he/she is saddled with responsibility of leadership and accountability. This implies that for educational institutions to fulfill their roles in bringing about positive changes in areas of knowledge, skills and attitudes of their beneficiaries, a lot has to be done by leaders of such institutions. However, this does not imply that the leader can do it alone, but he/she should be able to coordinate all the resources available to the school in order to enhance the achievement of common goals for which the school stands. The principals’ position could thus be compared to that of a man living in a “glass house” (Myer, 2002).
Managerial effectiveness which is often defined in terms of output implies what a manager achieves. That is, the ability of the organizational head to optimally utilize both human and material resources available to the organization in order to achieve organizational goals. Inyang (2008) defined managerial effectiveness as the leader’s ability to achieve desired results. He explained that how well he applies his/her skills and abilities in guiding and directing others determines whether he/she can meet those stated objectives effectively. He concluded that managerial effectiveness could be measured by the success a leader achieves. Results, according to him are generally believed to be influenced by the organization’s established culture. Thus, it is expected that a good leader must adapt to the organization’s culture and make sure that his/her skills align well with the organizational goals in order to achieve positive results. In a related development, Belo (2016) noted that there are linkages between governance of schools, possibilities of achieving stated goals and effective management. She thus concluded that the primary goal of principals should be how to enhance smooth running of schools with emphasis on managing activities even in the midst of pressure. By implication, this means that a principal would be regarded as effective if he/she is able to achieve school goals irrespective of all odds. Administrative challenges are the hindrances to the process of school administration.
That is, the problems encountered by principals in the course of carrying out their responsibilities and which could affect the attainment of school goals. Life is full of challenges and how well a person is able to cope and subdue such challenges will determine the success of the person. The principal as the head of administration in most secondary schools is often faced with myriads of challenges in performing his duties which could lead to non-accomplishment of stated goals. Some of these challenges are insufficient physical facilities, insufficient funds, teachers’ incompetence, ill-equipped library/ laboratory, indiscipline among teachers and students, incessant teachers’ transfer among others. Okeke (2008) summed it up that secondary schools in Nigeria are characterized by dilapidated infrastructures, obsolete equipment, out-dated books and journals and, above all, irrelevant curricula. All these factors make it impossible for the effective realization of their goals. In a related study, Otegbulu (2016) found out that the perceived challenges to effective administration in Imo state (which could also be applicable to Ogun State) are: insufficient funds, inadequate physical facilities, equipment and instructional materials, inadequate qualified school staff, inadequate staff motivation, indiscipline among teachers and students, frequent changes in educational policies among others. All these are believed to hinder principals’ managerial effectiveness. The importance of teachers’ competence in implementing the curriculum cannot be overemphasized because they are the backbone of educational activities as well as the drivers of education in all spheres of life. It is generally believed that it is what one has that can be given out. Indeed, some teachers show ignorance in their subject areas by teaching only the topics they understand in the curriculum and side tracking the difficult ones.
Such situation could have negative effects on the students by limiting their understanding of the contents of the subject and affecting their performance especially in external examinations. Yariv and Coleman (2005) contended that poor-performance among teachers cut across all nations and that school administrators usually have enormous difficulties in improving weak teachers’ performance or dismissing them. On the other hand, incompetence among teachers could be traceable to principals’ incapability of exercising their supervisory role and if care is not taken, other teachers could be negatively influenced. On the other hand, these effects could be inimical to the managerial effectiveness of the principal. Insufficient physical facilities have been found to be a major hindrance to principals’ managerial effectiveness. Statistics has shown that secondary school students’ population have been increasing progressively which has resulted in overcrowding the classrooms. This situation is prevalent in Ogun State secondary schools to the extent that they do not have enough physical facilities to conveniently accommodate all students. The resultant effect is congestion of classes, students not paying attention to teachers, unnecessary disturbance, inadequate seat for students, and this might even facilitate the outbreak of contagious diseases. All these conditions could be inimical to teaching-learning processes which could subsequently lead to non-attainment of school goals. The usefulness of funds in any meaningful organization cannot be under rated because it serves as the major vehicular means through which human and material resources could be harnessed in order to achieve the goals for which the organization stands. Olowoselu and Bello (2015) observed that poor funding of schools is a major problem of principals’ leadership ineffectiveness as it weakens leadership potentials.
In the school system, principals are often faced with paucity of funds as they are not allowed to collect extra money from the students irrespective of its purpose, and the meagre sum of money given by the state government as grants are not regularly released and they are even not enough to run the affairs of the school. Principals often experience shortfall in providing basic needs such as pieces of chalk, marker, pens, lesson notes, teachers’ time/movement book, stationaries, well equipped first aid box, fuelling and maintenance of generators, maintenance of computers, provision of toilet facilities for members of staff as well as convenient offices for teachers among others. All these are believed to be essential in effective running of the school, but can hinder principals’ managerial effectiveness if they cannot be provided as and when due. The importance of functional school library in the development of secondary education cannot be overemphasized because they serve as learning laboratories where total learning packages that could enrich teaching-learning processes are stocked. Edengbere in Owate and Okpra (2013) affirmed that school libraries in educational institutions such as pre-primary, primary and secondary schools are important as the life-wire and foundational upbringing of children. This is because they primarily stock materials that are of interest and developmental growth for young teenagers and youths. It could therefore be inferred that functional school library contributes to the development of teachers and students as it greatly contributes to the enlargement of their knowledge. Hence, non-functional school library can be likened to a house without a roof. Some of the libraries in Ogun State are stocked with outdated books, while some libraries do not have their books well-arranged due to insufficient space. In addition, teachers and students appear not to frequently make use of well-equipped school libraries probably because of ignorance or non-challant attitude. Be it as it may, non-functional library is a major administrative challenge that could impede attainment of school goals and subsequently hinder the managerial effectiveness of principals.
Teachers’ transfer is a useful part of centralized system of education, which can either be misused ignorantly or abused deliberately. It is believed that frequent transfer of teachers which could either be voluntary or involuntary during the session is harmful to the school system. This is because of the variance in methodologies and approaches of each teacher which makes it difficult to handle when the teachers are to teach same subject to same set of students. To worsen the situation, failure to immediately replace transferred teachers especially during the session gives room for inability to complete already scheduled topics for the term which can subsequently affect students’ performance in external examinations. Discipline could be said to be a central element in administration because it is considered to be one of the major attributes of an effective school as disciplined teachers and students are indicators of principals’ effectiveness. It is the ability of teachers and students to comply with schools’ stated rules, regulations and policies. A scenario in the state reveals that some teachers attend to their personal affairs at the expense of their primary assignment. For instance, some female teachers sell their goods and wares to other members of staff during school hours, some even sneaked out of school during official hours to hawk their wares rather than attending to their primary assignment on time. Similarly, some male teachers appear to engage students on their personal activities during break time and at times, this tends to affect part of the period after break. Some teachers also appear to be absent from school and classes while others neither write the subject diary nor the lesson plan. In a related development, truancy is a common thing among the students as some students come to school and attend classes at their convenient time without adhering to the school’s stipulated time table.
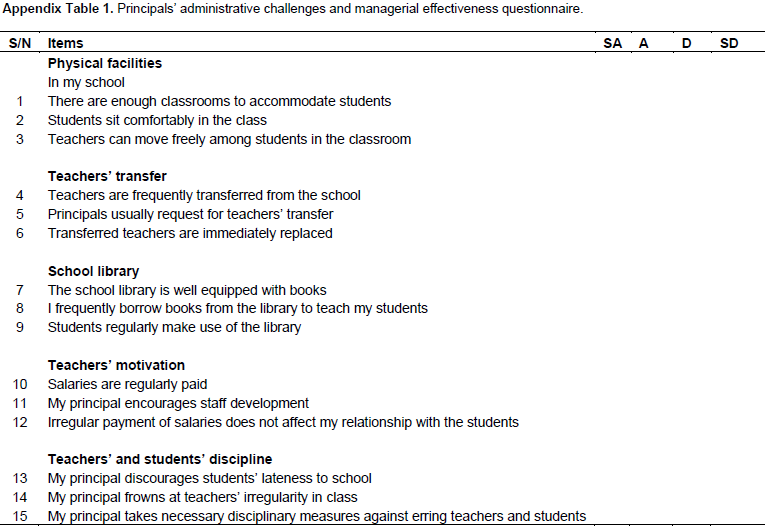
Some go to pop houses, cinemas, they do things as they like without any regard for the school programme. Torubel and Omemu (2015) summed it up that adolescents and youths of recent times behave in defiant and aggressive ways in and out of school setting such as disrupting school activities, bullying, drug consumption, cultism among others. They concluded that there is need to find solutions to these maladaptive behaviours if school goals are to be achieved. Inability to instil and maintain discipline among the teachers and students are indices of managerial ineffectiveness and this could have a negative impact on school administration. Existing evidence revealed linkages between principals’ administrative challenges and managerial effectiveness. Koontz and Weihrich (2005) suggested that managerial effectiveness be defined in terms of output rather than input and perceived as what a manager achieves irrespective of all odds rather than what he does. They concluded that once a manager is able to recognize this, his route to effectiveness is clear. It could be inferred from Koontz and Weihrich’s (2005) submission that administrative challenges could be a threat to principals’ managerial effectiveness if adequate care is not taken. It is against this background that the study investigated administrative challenges and principals’ managerial effectiveness. In Nigeria today, there is an increasing public fear and complaints about managerial effectiveness of principals, and this seem to escalate the incidence of cultism, delinquent behaviour, indecent acquisition of results among others. Failure in secondary school educational system has become a major concern to the government and other stakeholders and reasons such as principals’ leadership style, communication behaviours, teachers’ attitude among others have been adduced to this. However, administrative challenges ranging from paucity of funds, incessant teachers’ transfer, insufficient and non-availability of some physical facilities to indiscipline among teachers and students, ill-equipped libraries among others could also be a hindrance to principals’ managerial effectiveness. The problem of the study is therefore to search for a possible relationship between the impact of principals’ administrative challenges and managerial effectiveness (Appendix Table 1).

Research hypotheses
1. There is no significant relationship between administrative challenges and principals’ managerial effectiveness.
2. There is no significant relationship between incessant teachers’ transfer and principals’ managerial effectiveness.
3. There is no significant relationship between ill-equipped school libraries and principals’ managerial effectiveness.
4. There is no significant relationship between finance and principals’ managerial effectiveness.
5. There is no significant predictor of principals’ managerial effectiveness among the variables of administrative challenges.
The study adopted descriptive survey research design. The population of the study comprised all the 13,123 secondary school teachers in Ogun State. The sample for the study was 900 teachers selected from 35 secondary schools. The sample was drawn through randomly and proportionate random sampling techniques. In doing this, 9 Local Government Areas were randomly selected from the 20 Local Government Areas in the State. This was followed by proportionate selection of 5 secondary schools per Local Government Area, making 45 schools, 900 teachers were thereafter selected using simple random sampling technique at the rate of 20 teachers per school. A self-developed instrument of 30 items titled “Principals’ Administrative Challenges and Managerial Effectiveness Questionnaire” (PACMEQ) which was answered by teachers was used for the study. Both face and content validity were established by experts in the departments of educational management and tests and measurement in the Faculty of Education, Ekiti State University. A four point adapted Likert-scale of measurement was used thus: Strongly agree (SA), agree (SA), disagree (D), strongly disagree (SD). The reliability of the instrument was established through test-retest method. This was done by administering the instrument twice within an internal of two weeks to 48 teachers in two schools which were not part of the sample used for the study. The two sets of responses were correlated using Pearson’s Product Moment Correlation and a reliability coefficient of 0.78 was obtained. The hypotheses were tested using Pearson’s Product Moment Correlation. The results were held significant at 0.05.
Hypothesis 1: There is no significant relationship between administrative challenges and principals’ managerial effectiveness. Table 1 shows that r-calculated value of 0.204 was greater than r-table value of 0.195 at 0.05 level of significance. The null hypothesis was therefore rejected. This implies that there was a significant relationship between administrative challenges and principals’ managerial effectiveness.
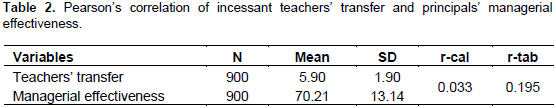
Hypothesis 2: There is no significant relationship between incessant teachers’ transfer and principals’ managerial effectiveness.
Table 2 reveals that r-calculated value of (0.033) was less than r-table value of 0.195 at 0.05 level of significance. Hence, the null hypothesis was not rejected. This implies that there was no significant relationship between incessant teachers’ transfer and principals’ managerial effectiveness.
Hypothesis 3: There is no significant relationship between ill-equipped school libraries and principals’ managerial effectiveness. Table 3 shows that the value of r-calculated (0.364) was greater than the value of r-table (0.195) at 0.05 level of significance. The null hypothesis was thus rejected. This implies that there was significant relationship between ill-equipped school libraries and principals’ managerial effectiveness.
Hypothesis 4: There is no significant relationship between finance and principals’ managerial effectiveness. Table 4 shows that r-calculated value of 0.353 was greater than r-table value of 0.195 at 0.05 level of significant. The null hypothesis was therefore rejected. This implies that there was significant relationship between finance and principals’ managerial effectiveness.
Hypothesis 5: There is no significant predictor of principals’ managerial effectiveness among the variables of administrative challenges. Table 5 reveals that variables of administrative challenges jointly and significantly contributed to principals’ managerial effectiveness (F = 1.355, P < 0.05). The null hypothesis was therefore rejected. The single best predictor of managerial effectiveness is finance with a beta weight of 0.121 (12.1%) while physical facilities with a beta weight of 0.006 (0.6%) is the least predictor of principals’ managerial effectiveness.
The study revealed a significant relationship between principals’ administrative challenges and their managerial effectiveness. This implies that problems besieging principals have impact on their ability to attain school goals. Probable reason for this might be because of the general belief that for a manager to achieve effectiveness, the physical environmental and other circumstances in the school must be encouraging. This study confirms the submission of Ikgbusi and Iheanacho (2016) that a correlation exists between administrative problems and management of school system. Results also suggest that there is no significant relationship between incessant teachers’ transfer and administrative effectiveness of principals. Reason for this might not be unconnected with principals’ ability in using teachers on ground to assist in areas with inadequate personnel. This result is at variance with Muyingo (2010) and Farzana et al. (2012) who found out that incessant teachers’ transfer has effect on the management of school. A significant positive relationship between ill-equipped school libraries and principals’ managerial effectiveness was also found. This implies that putting up a well-equipped school library as well as encouraging its use goes a long way in aiding principals’ managerial effectiveness. Reason for this might be because of the assumption that well equipped libraries could enhance better understanding of what the students were taught and as well afford them the opportunity of reading ahead of their teachers. Finding of this study is in congruence with Whitefish (2004) and Omera (2013) who contended a correlation between well-equipped libraries and attainment of school goals. A significant relationship between finance and principals’ managerial effectiveness was also suggested. Implication of this is that money is a sine qua non for principals’ managerial effectiveness. Reason for this might not be unconnected with the general belief that money is one of the vehicular means of achieving success in every organization. This corroborates Olowoselu and Bello (2015) and Otegbulu (2016) who established a relationship between funds and leadership effectiveness of secondary school principals. Finally, the hypothesis which sought to find the best predictor of principals’ managerial effectiveness among the variables of administrative challenges found out that finance is the best predictor with a beta weight of 0.121 while physical facilities with a beta weight of 0.006 is the least predictor. This might be due to the general belief that money is an important tool that aids smooth running of school administration and subsequently, the attainment of school goals.
The findings of this study have led to the conclusion that administrative challenges are critical problems of principals’ managerial effectiveness. On the basis of the conclusion, the following recommendations were made:
1. Government should give out its supportive arms by releasing grants to the school as and when due and also allow them to collect meager sum of money either on termly or yearly basis which should solely be spent on developmental projects.
2. Within the limited resources available to schools, principals should endeavour to stock the libraries with necessary textbooks.
3. Seminars, workshops and conferences should regularly be organized by the Ministry of Education and Teaching Service Commission for principals on how to reduce to the barest minimum level, those variables (funds, ill-equipped library and teachers’ competence) that hinder their managerial effectiveness.
The authors have not declared any conflict of interests.