Full Length Research Paper
ABSTRACT
When the desire that grows in a person is balanced with will and ability, self-confidence grows, especially when someone gets motivation and support from seeing that he can develop more than he thinks. In entrepreneurship, it is necessary to have self-confidence; self-confidence will provide the motivation needed for the business to thrive. Without a sense of self-confidence, every effort made will be in vain. This study reveals one determining factor for entrepreneurial success is the presence of self-confidence, and self-confidence can be categorized into several variables, including feelings, beliefs, perceptions, and expectations. Many successful efforts are due to a sense of optimism, where every failure is an opportunity to get up and move forward. Without a definition of confidence success in entrepreneurship is impossible. The results show that there is a positive and significant effect of entrepreneurship self-efficacy on entrepreneurial intentions.
Key words: Vocational education, entrepreneurship, self-efficacy.
INTRODUCTION
Vocational education aims to prepare students to become productive humans, able to work independently, to fill existing job vacancies according to the competencies in the expertise program they choose in order to be independent and productive (Rintala and Nokelainen, 2020; Yoto, 2016). Vocational high school students need to change their way of thinking by not just hoping to become employees, but becoming someone who opens new jobs for others, because currently, competition in the business world is very tight along with the number of jobs that are not proportional to the number of workers (Rainie and Anderson, 2017). This is evidenced in the online site written by the Selasar Editor, which revealed that according to the Central Statistics Agency (BPS) as of February 2014, there was open unemployment of 5.7% or 7.15 million people. The figure of 7.15 million people is mostly filled with young unemployed, between 19-24 years. The National Development Planning Agency (Bappenas) also noted that the number of unemployed youths between 15-29 years in Indonesia is about 19.9%. Educational institutions play an essential role in fostering student interest in entrepreneurship. According to Harackiewicz et al. (2016), interests are feelings, hopes, convictions, prejudices, fears, or other tendencies that lead individuals to confident choices. Meanwhile to Djaali (2013), interest is a sense of preference of concern in something or activity without being asked. Someone who has an interest in an object tends to pay great attention to that object.
Entrepreneurship according to Elfving (2008) is the process of creating something new at the value of using the time and effort required, bearing financial, physical, and social risks that accompany, receiving the resulting monetary rewards, as well as personal satisfaction and freedom. According to Nasution et al. (2021), entrepreneurs are not just traders but there are much deeper meaning on human mentality, self-confidence, time efficiency, creativity, grit, tenacity, seriousness, and morality in running an independent business. The ultimate goal is to prepare individuals and societies to live correctly as humans. Interests play a significant role in the lives of students and have a substantial impact on attitudes and behaviors. Students who have an interest in something tend to have an interest in knowing and learning things related to such interest without coercion. A person is said to have a high interest in entrepreneurship due to various aspects of his personality such as character, attitude, and behavior. According to Apriyani et al. (2019), the characteristics of entrepreneurship have six critical components, namely self-confidence, results-oriented, risk-taking, leadership, originality (innovative, creative, and flexible), and future-oriented. According to Suhartini (2011), several factors influence interest, namely: internal driving factors, which are stimuli from the environment or scope according to one's wishes or needs; social motive factors, what is a person's interest in objects that are influenced by elements from within humans and motives, social, emotional and feeling aspects which influence the object.
The existing entrepreneurship will not run if it is not balanced with the self-efficacy of students in entrepreneurship to give birth to new entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurship self-efficacy that students have will give them maximum results if students believe in themselves that they are capable. Not all students have high entrepreneurship self-efficacy, because most students feel unsure. Entrepreneurship belief in oneself will foster one's entrepreneurial intention. If someone is not sure about the abilities they have, it is unlikely that the person will have entrepreneurial intentions. Entrepreneurship intention begins before students decide to be entrepreneurs, then students will be committed to the decisions that have been made. The purposes can also bridge the gap students in their subsequent actions. Self-efficacy is a person's belief or confidence in his ability to do something. This self-efficacy is very important for self-development.
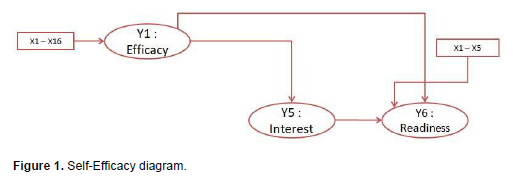
Self-efficacy seems to be very much needed for everyone in entrepreneurship. This confidence will makesomeone believe they can carry out and organize all the required actions in situations that have good prospects and profitable opportunities. Everyone seems to need self-efficacy, especially when they enter the world of work. Self-efficacy is a person's belief in his or her ability to perform tasks or activities needed to achieve specific results. Bandura explained that self-efficacy is the result of a cognitive process in the form of decisions, beliefs, or awards about the extent to which a person estimates his or her ability to complete or carry out tasks or achieve the expected results. Self-efficacy rests on a person's belief. A person with self-efficacy believes that they are capable of doing something to change the events around them. In contrast, a person with low self-efficacy considers himself to be unable to do anything around him. In difficult situations, people with low efficacy tend to give up easily. Meanwhile, people with high self-efficacy will strive to overcome obstacles that get in the way. Several previous studies have discussed self-efficacy in terms of developing entrepreneurship, especially in vocational education. Yulianingsih et al. (2013) in their research showed that there was a positive and significant relationship with a moderate level of correlation between entrepreneurial knowledge and interest as well as self-efficacy in entrepreneurship for class XII accounting students of SMK Negeri 1 Sukoharjo in the 2012/2013 academic year. This means that students 'interest in entrepreneurship will increase if students' entrepreneurial knowledge increases. Marini and Hamidah (2014) shows that self-efficacy has a positive and significant effect on interest in entrepreneurship, with a correlation coefficient (rx1y) of 0.440 and p<0.05. In line with this research, Bernstein and Carayannis (2012) concluded that "it is proposed that a positive relationship exists between self-efficacy for having an entrepreneurial career with interest in majoring in entrepreneurship" (Figure 1).
This means there is a positive relationship between self-confidence and interest in a career as an entrepreneur in the entrepreneurship department. Therefore, based on the explanation that has been put forward, the author is interested in examining the self-efficacy of the most crucial factor in entrepreneurship, especially in vocational research. This paper hopes to contribute in terms of scientific development and become the basis for research development. The purpose of this study is to provide information sources, especially in terms of the role of self-efficacy in supporting student success in entrepreneurship, especially in vocational education. Also, this study is an initial study on the development of doctoral dissertation research conducted by researchers.
PROBLEMS OF STUDY
The problems that will be studied in this research are: how significant is the influence of self-efficacy as a
supporting factor for student success in entrepreneurship and how is the impact of self-efficacy on entrepreneurship development in vocational education? Self-efficacy is related to one's beliefs for exert personal control on motivation, cognition, affection for the social environment (Bandura, 1997). Self-efficacy is the belief that a person is capable of carrying out tasks, achieving goals, or overcoming obstacles. Individuals tend to avoid or even run away from situations that they believe the individual is unable to deal with. Self-efficacy is self-perception of how well one can function in certain situations; self-efficacy is related to the belief that oneself can take the expected actions (Alwisol, 2009).
Self-efficacy is a complete belief in yourself, optimism and hope to solve problems without feeling hopeless. When an individual is faced with the stress that will arise, his self-efficacy ensures a reaction to a situation between emotional reactions and his efforts in facing adversity. The self-efficacy possessed by the individual can make the individual deal with a variety of situations (Patton, 1998). Self-efficacy is a person's belief about his chances of accomplishing a particular task (Kreitner and Kinick, 2003). Self-efficacy is a person's belief that he will be able to carry out the required behavior in a task. Referring to some of the opinions above, it can be concluded that self-efficacy is a person's belief in one's ability to carry out tasks, achieve goals, or overcome obstacles (Prakoso, 1996).
Self-efficacy is formed by four sources of information, one of which is successful experience. In human life, the success of solving a problem will increase self-efficacy, on the other hand, failure will decrease self-efficacy (especially in self-efficacy time has not been established in a person). For self-efficacy to be established, one must experience tough challenges, so he could finish them with persistence and hard work (Bandura, 1997). The development of self-efficacy in addition to being determined by the success and failure that has been done is also determined by errors in self-assessment. If in everyday life what is always remembered is poor appearance, then the conclusion about self-efficacy will be low. Conversely, even though failure is often experienced but continuously trying to improve performance, self-efficacy will increase. Collection of past experiences will determine self-efficacy through cognitive representations, which include a memory of the frequency of success and failure, temporary patterns, and the situations in which success and failure occur (Bandura, 1997).
The role of thinking ability in the development of self-efficacy is quite large because high intelligence people will be better able to remember and analyze events that have been experienced so that the conclusions made will be more accurate. Self-efficacy in each individual will differ from one individual to another based on three aspects. This is expressed by a self-efficacy scale based on the aspects of self-efficacy put forward by Bandura, namely task difficulty level, area of duty and level of stability, confidence, strength (Bandura, 1997):
Task difficulty level (Magnitude)
This aspect relates to the degree of difficulty of the task. If the tasks assigned to individuals are arranged according to their level of difficulty, then differences in individual self-efficacy may be limited to easy, medium, and difficult tasks, according to the limits of the perceived ability to meet the behavioral demands required at each level. To know the reflection of a person's level of self-efficacy in carrying out a task, it is necessary to measure it against every demand for a task that must be done by someone. In this study, to measure the level of self-efficacy, a person can choose from five gradient degrees of self-efficacy. These gradients include: completely unsure of being able to do; not sure of being able to do; sometimes being sure of being able to do; confident of being able to do; and very confident of being able to do.
Area of duty (Generality)
This aspect relates to the broad field of behavioral tasks in which individuals feel confident in their abilities. In measuring a person's self-efficacy in performing a task, it is not only limited to one aspect, but the measurement of self-efficacy is measured from several aspects. The aspects in this research are used as a reference in measuring one's self-efficacy, including social resources, academic competence, self-regulation in learning, utilizing free time and extracurricular activities, self-efficacy in self-regulation, and the expectations of others.
Level of stability, confidence, strength (Strength)
This aspect relates to the strength level of an individual's belief or expectation regarding his ability. To determine the strength level of a person's self-efficacy, it is necessary to measure using a self-efficacy scale. This self-efficacy is useful for describing the difference in the strength of one's self-efficacy with others in performing a task.
Luthans states that self-efficacy can directly impact the following (Luthans, 2005): selection of behavior- decisions will be made based on how efficacy a person feels against choices, for example, work assignments or career fields; effort motivation- people will try harder and try more at a task where their self-efficacy is higher than those who have low self-efficacy; endurance- people with high self-efficacy will be able to get up and survive when faced with problems or failures, while people with low self-efficacy tend to give up when facing obstacles; facilitative thinking patterns- efficacy ratings influence self-talk as a person with high self-efficacy might say to himself, "I know I can find a way to solve this problem". Some people with low self-efficacy may say to themselves, "I know I cannot do this, I don not have the ability”; stress resistance- people with low self-efficacy tend to experience stress and laziness because they think of failure, while people with high self-efficacy enter stressful situations with confidence and certainty and are thus able to withstand stress reactions. Researchers have documented a strong tie between high self-efficacy and success in a wide variety of physical and mental tasks. Conversely, people with low self-efficacy are associated with a condition called learned helplessness (distrust of one's ability to control a situation), a drastically weakened belief so that a person has no control over their environment (Kreitner and Kinicki, 2003).
Based on the description above, it can be concluded that self-efficacy has an impact on a person's life. The impact of self-efficacy, among others, is that individuals can choose the right behavior, have high motivation in trying, can survive when facing problems, have facilitative thinking patterns, and are more resistant to stress. Individuals who have high self-efficacy will tend to choose to be directly involved in doing a task, while individuals who have low self-efficacy tend to avoid the task. Individuals who have high self-efficacy tend to do a particular task, or even though the tasks are difficult. They do not view assignments as a threat they must avoid. Those who fail to do something, usually quickly regain self-efficacy after experiencing that failure.
Individuals who have knowledge and fail, fail because of lack of of hard effort, knowledge, and skills. Individuals who have low self-efficacy will stay away from difficult tasks because they are seen as a threat to them. Such individuals have low aspirations and low commitment to achieving the goals they choose or set. Individuals who have low self-efficacy think about how to deal with difficult tasks. They are also slow to fix or regain self-efficacy when faced with failure. Based on the above opinion, it can be concluded that individuals who have high and low self-efficacy have the following characteristics (Permana et al., 2016): High self-efficacy- tend to be directly involved in doing a task. Tend to do certain tasks, as well as difficult tasks. Regard failure as a result of a lack of effort, knowledge, and skills and is persistent in trying. Believe in one's abilities with little doubt and likes to find new situations; Low self-efficacy- tend to avoid assignments. Doubt his abilities. A difficult task is seen as a threat. Sluggish in fixing yourself when you fail, weak aspirations and commitment to duty, do not think about how to deal with problems and does not like looking for new situations.
From business activities carried out by the community, either small or large scale, can be categorized according to their characteristics and character, including into entrepreneurial activities or not. The following are the characteristics and characteristics of entrepreneurship (Suryana, 2001):
1. Confidence means that in managing business activities, an entrepreneur must have confidence that the business carried out is sure to be successful. It does not depend on other people in carrying out its activities and is managed individually, and always has a high optimistic spirit.
2. Oriented to tasks and results, meaning that business activities goals carried out to achieve with profit orientation. For this reason, business activities must be carried out diligently, full of courage, and determination to work hard and have strong drive, energetic and initiative in running its business.
3. Taking risks, entrepreneurial activities are indeed required to take reasonable risks from their business activities, the higher the risk, the greater the possibility of benefits and the smaller the risk, the less likely the benefits will be obtained.
4. Leadership, in leading business activities, must be clever, socialize/communicate with all levels of society or stakeholders and can receive suggestions and criticism for the progress of their business activities.
5. Originality, meaning that business activities are always carried out developed with creations that are new and easy to adjust to market developments/market segments.
6. Oriented to the future, to develop business activities should always take advantage of scientific developments knowledge, and technology so as not to be left behind with competitors.
In carrying out entrepreneurial activities, an entrepreneur is required to know the type and level of entrepreneurship to know his position in entrepreneurship. The types and levels of entrepreneurship are as follows (Winarto, 2011):
1. Innovating Entrepreneurship- experimented aggressively, skillfully practiced attractive transformations. Experiments should always be carried out to find the updates that will be later transformed into the real activities of business activities to keep up with the demands of consumer demand.
2. Imitative Entrepreneurship- copying successful innovations from innovative entrepreneurs. In addition to efforts to find new things to develop its business, it can also adopt successful innovations from its predecessors, although it must also be considered the possibility of saturation points from the output of previous renewal products.
3. Fabian Entrepreneurship- an utterly cautious attitude and an attitude of skepticism but an immediate one carry out the imitations it becomes very clear, if they are not doing so, they will lose their relative position in the industry concerned. This attitude determination is to avoid falling behind with the existing industrial position there is.
4. Drone Entrepreneurship- drone means laziness. Refuse to take advantage of opportunities to carry out changes in the production formula even if it will result in them losing money compared to other producers. Slowness and lack of communication with other parties about changes and updates that occur will cause significant losses.
5. Parasitic Entrepreneurship- in many developing countries there is still another type of entrepreneurship known as Parasitic Entrepreneurship, in the context of economics it is referred to as rent-seekers.
To be able to carry out entrepreneurial activities, it is necessary to know the stages in entrepreneurship. In general, the stages of doing entrepreneurship (Winarto, 2011):
1. The initiating stage- this is the stage where a person intends to make efforts to prepare everything that is needed, begins by looking at what new business opportunities might be open to new business, make acquisitions, or do franchising. Also choose the type of business to be carried out whether in agriculture, industry/manufacturing/production, or services.
2. The stage of carrying out the business or summarized by the "road" stage- here an entrepreneur manages various aspects related to his business, including aspects which include financing, human resources, ownership, organization, leadership includes how to take risks and make decisions, marketing, and doing evaluations.
3. Maintain effort- at this stage the entrepreneur has based the results that have been achieved perform an analysis of the progress achieved to be followed up following the conditions at hand.
4. Develop a business- here if results are obtained classified as positive or experiencing development or can survive, and then business expansion is one possible option taken.
Entrepreneurs are divided into three levels, namely early entrepreneurship, tough entrepreneurship, and entrepreneurship superior. It is divided into three groups: Administrative Entrepreneurs, Innovative Entrepreneurs, and Catalyst Entrepreneur. Entrepreneurship triggers are influenced by internal factors and external factors. Becoming a successful entrepreneur requires certain steps. The entrepreneurial process model consists of an initial (piloting) phase and a phased growth. Other factors that cannot be ignored are the factors that cause entrepreneurial failure and the advantages and disadvantages of entrepreneurship.
Based on literature analysis related to entrepreneurship, it is known that aspects that need to be considered in doing entrepreneurship are (Winarto, 2011):
1. Looking for new business opportunities- the length of time the business was carried out, and the type of business ever done.
2. Financing- funding, the amount and sources of funds
3. Human Resources- labor used.
4. Ownership- roles in conducting business
5. Organization- division of labor among the workforce that is owned
6. Leadership- honesty, religion, long-term goals, process managerial (POAC)
7. Marketing- location and place of business.
Entrepreneurship provides several benefits including (Waspada, 2004): increase productivity; increase economic growth and create jobs; creating new technologies and creating new products and services. Many entrepreneurs take advantage of opportunities by creating new products or services. Even if they still defend the old product, the product is an existing product repaired. Many entrepreneurs also develop technology new to producing goods; drive innovation. Though it usually does not create anything new, they can develop methods or products innovative; helping large business organizations. Big businesses often acquire components from small producing companies these components. Big companies do not produce goods and this is because it is not very efficient to produce small components with a small market.
Entering the present decade, the development of the economic environment in the world has undergone rapid change and is leading to stabilizing a more open form of the market economy. During such a situation, the problem that faces the Indonesian nation is how the activities of our economic actors can keep up with these changes and create high competitiveness in facing the global market. One of the most important factors in preparing the toughness of national economic competitiveness is improving the quality of human resources, especially those active as economic actors. One of the efforts to achieve independence and resilience national economy is through the development, stabilization of attitudes, behavior, and skills as well as entrepreneurship. This is because the development of national entrepreneurs will be driving the wheels of the national economy and spurring growth national economy. This effort needs to be supported by all good groups from elements of government, society, and the business world in a directed and sustainable manner.
An entrepreneur is said to be successful if he meets the following criteria (Kasmir, 2007):
1. Have clear vision and goals. This function is to guess where the steps and directions are going so that the entrepreneur can know what steps the entrepreneur should take.
2. Initiative and always proactive. This is a fundamental trait where entrepreneurs are not just waiting for something to happen, but first to start and look for opportunities as a pioneer in various activities.
3. Achievement-oriented-Always successful entrepreneur pursuit of achievement that is better than previous achievements. Product quality, services provided, and customer satisfaction are the main concerns. Every time all business activities are run is always evaluated and must be better than previous.
4. Dare to take risks. This is a must-have trait for an entrepreneur anytime and anywhere, both in terms of money and time.
5. Hard work. Employer working hours are not limited to time; where there is an opportunity there he comes. Sometimes a businessman it is difficult to manage his working time. His mind was always thinking progress of his business. New ideas always pushed him to work hard to make it happen. There are no words difficult and there are no problems that cannot be resolved.
6. Responsible for all activities carried out, good now and in the future. The responsibility of an entrepreneur is not only material but also moral to various parties.
7. Commitment to various parties is a characteristic that must be adhered to and must be adhered to. Commitment to do something is indeed an obligation to immediately pay for the realization.
8. Develop and maintain good relationships with various parties, whether directly related to that business whether it is run or not. Relationships are necessary to execute, among customers, government, suppliers, and the wider community.
From the analysis of experience in the field, the main characteristics of entrepreneurship to be successful can be summarized in three attitudes, namely (Winarto, 2011):
1. Honest, in the sense of being brave enough to state the real conditions of the business being run, and willing to carry out its business activities according to its capabilities. This is necessary because this attitude tends to make buyers have high trust in entrepreneurs so that they are willing to become customers in the long term.
2. Have long-term goals, in the sense of having a picture of clear information regarding the final development of the business being carried out. This is to be able to provide great motivation for entrepreneurs to be able to do work even though at the same time the expected results have not been obtained.
3. Always be obedient to pray, which is submission to God to ask for what you want and accept whatever results you get. In another language, it can be stated that "man tries, but God is the one who determines!" therefore praying is one of the therapies for business maintenance to achieve goals.
Dan Steinhoff and F. Burgess suggested several characteristics needed to achieve the building-up of entrepreneurial success, as follows (Suryana, 2003): have the vision to achieve goals; can anticipate the risk of time and money; plan, organize and follow up; work hard; build trust in customers, employees, suppliers, and others; responsibility for success.
Based on the above opinion, it appears that there are several things an entrepreneur must have to be successful in running a business. First, he must have a vision and goals of the business which he is pioneering. Second, after his business is running, he must be able to anticipate risks that may arise, both from a time perspective and from a financial perspective. Third, being able to plan everything that will be done, organize employees and follow up on any problems or opportunities that exist. Fourth, must be willing to work hard.
A business can be successful or a failure depending on the previous business plan. Business planning describes analysis and feasibility studies that include studies of raw materials, processing to marketing. In business planning, it is also necessary to conduct a cash flow study (cash flow) which describes the profits that can be obtained each year so that expenses and income (Break-Even Point) can be estimated with certainty. For those of us who want to start a small business on a home industry scale, business planning is also very important. There are two planning activities, the first which includes tasks, such as making contact with bankers as a source of funds (if funds are from banks), accountants, and lawyers if our business will be established in a certain legal entity. Second, planning related to routine business activities, such as preparing monthly financial reports, monitoring and revising budgets, allocating production time, and marketing products.
In general terms, before starting as an entrepreneur, we must prepare and plan capital, equipment used for production, standard manufacturing procedures for production goods, product raw materials, raw material suppliers (if just starting a business means the location for taking raw materials), executors, financial holders, marketing actors. , determine the number of goods to be produced, sales targets, target consumers, product prices, expected profits, solutions if experiencing obstacles, to small things such as packaging, product names, and label forms. After everything has been prepared, then we can start a business which of course begins with high intentions and motivation, as well as a prayer that our efforts will be successful.
After the home industry that we run lasts one week, we need to check how smooth the marketing of our products is. If it turns out well, and the benefits we expect are met, then we can continue the business; likewise the following week. So, when we start a new business, check the marketing/sales of our products on the market as often as possible. But after running for months and it turns out that the results are always following our expectations (getting a profit), then checking can be done per month because that means our business prospects are bright.
Meanwhile, to be able to reach the peak of an entrepreneurial career, one must go through eight steps, consisting of (Alma, 2011): work hard (capacity for hard work); collaborating with other people (getting things done with and through people); good appearance; self-confidence; good at making decisions; want to increase knowledge; ambition to move forward. Successful entrepreneurs have a standard of achievement high. The entrepreneurial potential can be seen as follows (Masykur, 1994; Winardi, 2003): innovative capabilities; tolerance of ambiguity; the desire to excel; realistic planning capabilities; goal-oriented leadership; objectivity; personal responsibility; adaptability (flexibility); ability as organizer and administrator; high level of commitment (survival).
One of the ways to evaluate the success of a business can be assessed by the amount of income. In the economic sense, there are various kinds of concepts of income, it depends on which point of view we see it. As for what is meant by the income of each individual, namely the income received by an entrepreneur, which is often called the entrepreneur's profit. Gardner Ackley suggests the following definition of individual/someone's income: “An individual's income can be defined as the amount of income obtained from production services that he delivers at a certain time or from his assets; national income is not more than the sum of all individual income" (Ackley, 1961). J. Schumpeter's Dynamic Theory, Profits are found in life dynamic economy and obtained by dynamic entrepreneurs as well (Waspada, 2004). Dynamic entrepreneurs who are also known as the captain of entrepreneurs, namely pioneering entrepreneurs, who dare to take new paths, use new techniques and try new production methods, will receive benefits ahead of other entrepreneurs. They will receive supernormal profit, while other entrepreneurs will only profit normally. It is only in the long term that other entrepreneurs will emulate it to use new production techniques and methods. Thus, the supernormal profit will be lost. Meanwhile, Profit as a risk premium from F. Knight in his book "Risk Uncertainty and Profit" suggests that profit is linked with uncertainty. Therefore, entrepreneurs should have "perfect for sight" (Waspada, 2004). For the courage to take the risk and their keen view of the future, then they should receive some compensation for their skills. With this in mind, the success of profit is largely determined by entrepreneurial ability, courage to take risks is a view of the future, so that small business can develop themselves in global competition and develop themselves in creating a good competitive climate. Of course, this success is expected to be able to minimize the level of risk by properly analyzing future uncertainty patterns.
Extrinsic success is a measured success with lots of materials, achievements, and other extrinsic factors. Neither achievement nor material wealth is an indication of success. To regard life to produce worldly possessions is a short-term goal. Human capital is a basic trait that supports success in entrepreneurship (Austhi, 2017). This trait is formed and emerges from within itself that other people do not always have, namely the right combination and composition of a tough and unyielding attitude, and the ability to cope with difficult times in various situations. Social capital is where having a positive social environment and supporting the development and journey of a person in pursuing an entrepreneurial career, namely friends and relatives, mothers who can support, develop, inspire, and love that person wholeheartedly (Austhi, 2017). Reputational capital is where an entrepreneur has a positive reputation to give a strong character in every work he has (Austhi, 2017).
METHODS
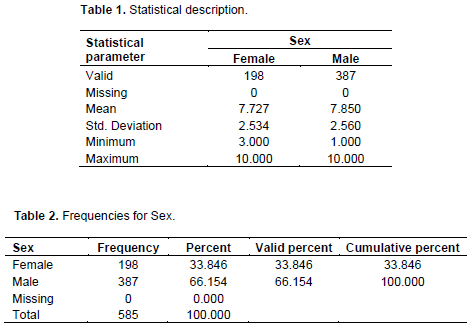
In this study, researchers used a quantitative research method approach. By using a sample population of 300 students as the sample of the course, as shown in Table 1. The sample population in this study was obtained from the air transportation school consisting of 7 populations with a sample value of 585 respondents. Among them are 198 women and 387 men, resulting in the following calculation.
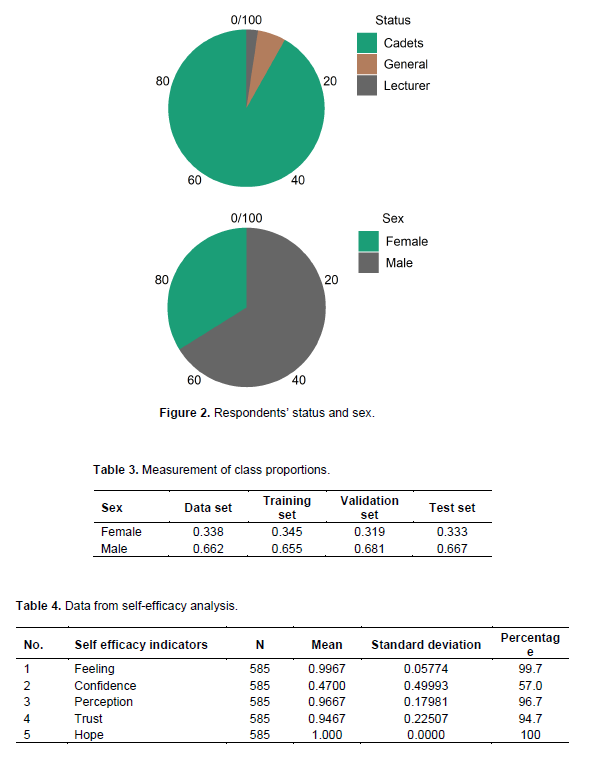
Respondents’ status, sex and class proportions
Respondents were drawn from the productive age range between 17 and 25 years, consisting of students at the polytechnic aviation Surabaya, from 7 study programs with a random sample of men and women as shown in Table 2, with their respective status and sex are presented in Figure 2. In this measurement (Table 3), it can be seen that the test data for women are 0.338 and for men 0.662, resulting in a training set of 0.345 for women and 0.655 for men, until it is known that the test set produces 0.333 for women and 0.667 for men. The research variables consisted of self-efficacy which consisted of independent variables (X1): Feelings (X2): Beliefs (X3): Perceptions (X4): Trust and the dependent variable (Y): Expectations.
Data collection and analysis
Data collection techniques are a method used to obtain the data needed in a study. To get the required data, namely documentation, and questionnaire techniques, the analysis technique uses descriptive analysis in the form of a percentage which is analyzed by Microsoft Excel and SPSS 12. The data analysis technique begins by determining the percentage score as in equation (1).

Where, A% = percentage scores; n = value obtained; N = total value
Meanwhile, for the analysis confidence variable, several questions were used, each of which had a score of 1 to 4.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this study, researchers used a quantitative research method approach. With the subject of self-efficacy, including feelings, beliefs, perceptions, beliefs, and expectations as the results of the analysis are presented in Table 4. Based on the results of the analysis in Table 4, it can be seen that only 3% have the feeling of wanting to pursue or enter into the world of entrepreneurship. In comparison, 99.7% do not want to join or enter the world of entrepreneurship. From the confidence table, it can be seen that only 53.0% lack confidence to do entrepreneurship while 47.0% can do entrepreneurship. Furthermore, it is found that only 3.3% have a good perception of the willingness to implement Entrepreneurship Moderate 96.7% lack a good perception of Entrepreneurship, meaning they want to but only think or still have a sense of concern to start entering the world of entrepreneurship, that maybe fear of failure. Furthermore, it can be seen that 5.3% of students have the confidence to succeed in entrepreneurship and 94.7% do not believe it. From the results of the analysis in, it can be seen that the indicators of trust play an important role in supporting success in entrepreneurship. Austhi (2017), in his writing, reports that success can be translated into a feeling of satisfaction at their work, which has the freedom to create their atmosphere and work environment. Success is measured by the value of each individual, not just their market share, income stream, or profit margin. Meanwhile, Wulandari and Muafi (2021) reports that with self-efficacy, the power for more significant business can be obtained. The stronger the feeling of self-efficacy and the greater the persistence, the higher the likelihood that the activity is selected and carried out successful. Aside from the feeling aspect, confidence has a smaller percentage compared to other indicators, with a percentage of 57.0%. This is most likely influenced by the psychological state of students who are not ready and still hesitant in running a business. This doubt can become a part that makes a prospective entrepreneur must think carefully about the concept of the company being built. This is in line with what was stated by Wulandari and Muafi (2021) in his study, that the lack of confidence in students' abilities causes these students to feel doubtful and afraid of failure when facing obstacles and do not dare to take risks. Also, with self-efficacy, the power for more tremendous effort can be obtained. The stronger is the feeling of self-efficacy and the greater the persistence, the higher the likelihood that the activity is selected and carried out successfully. In the aspect of perception, trust, and hope also hold a high percentage with a value of 96.7% (perception), 94.7% (faith), and 100% (expectation). Therefore, from the results of the analysis, it is obtained that the sample population has a hope of being able to enter the world of entrepreneurship. Still, it all depends on the factors of the variables that the researchers have proposed, including feelings, beliefs, perceptions, and expectations.
CONCLUSION, LIMITATION AND FURTHER RESEARCH
This research has several limitations such as the study cannot be implemented directly into business ventures. For this reason, further research needs to consider related aspects of several variables that are suitable to be developed into the world of entrepreneurship, including age, education level, and ability, as control variables, further research so that students can consider being able to enter the world’s entrepreneurship, self-efficacy, attitudes towards entrepreneurship, and perceived behavioral control. In other words, entrepreneurial self-efficacy, attitudes towards entrepreneurship, and perceived behavior control have mediated the relationship between subjective norms and entrepreneurial intentions, also, our results show that the relationship between entrepreneurial self-efficacy and entrepreneurial intentions are mediated by attitudes towards entrepreneurship and perceived behavioral control. Thus, two research questions have been answered clearly. Useful to examine further research should expand the research model by adding new variables such as gender, a field of study, entre-preneurship education, an entrepreneurial ecosystem to enrich and contribute to the literature review and entrepreneurial practice.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors have not declared any conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors appreciate the respondents for offering their time to carry out the survey.
REFERENCES
|
Ackley G (1961). Macroeconomic Theory, Jakarta: UI press: University of Indonesia Publisher. |
|
|
Alwisol (2009). Personality psychology revised edition. Malang: PT. UMM, Press. P 287. |
|
|
Apriyani Y, Haryono SEQ ZM (2019). The Effect of Self-Learning, Entrepreneurship Competence and Entrepreneurship Orientation on Micro Business Performance in the Special Province of Yogyakarta. |
|
|
Austhi D (2017). Entrepreneurial Motivation and Entrepreneurial Success in Female Entrepreneurs Anne Avanite. AGORA 5(1). |
|
|
Bandura A (1997). Social learning theory. In: Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs. |
|
|
Bernstein AT, Carayannis EG (2012). Exploring the value proposition of the undergraduate entrepreneurship major and elective based on student self-efficacy and outcome expectations. Journal of the Knowledge Economy 3(3):265-279. |
|
|
Djaali (2013). Educational Psychology. Jakarta: Earth Literacy. |
|
|
Elfving J (2008). Contextualizing entrepreneurial intentions: a multiple case study on. Entrepreneurial cognition and perception. Abo Forlag Academy. |
|
|
Harackiewicz JM, Canning E A, Tibbetts Y, Priniski SJ, Hyde JS (2016). Closing achievement gaps with a utility-value intervention: Disentangling race and social class. Journal of personality and social psychology 111(5):745. |
|
|
Kasmir (2007). Kewirausahaan, PT Raja Grafindo Perkasa, Jakarta. |
|
|
Kreitner Rd, Kinicki A (2003). Organizational Behavior, Fifth Edition, McGraw- Hill Higher Education. |
|
|
Luthan (2005). Organizational Behavior, New Rok, Mc. Graw-hil companies, hlm. P 186. |
|
|
Marini CK, Hamidah S (2014). The influence of self-efficacy, family environment, and school environment on entrepreneurial interest in Jasa Catering Vocational High School students. Journal of Vocational Education 4(2):195-207. |
|
|
Masykur W (1994). Entrepreneurship: A series of lectures, Gunadarma. Jakarta. |
|
|
Nasution MDTP, Rafiki A, Lubis A, Rossanty Y (2021). Entrepreneurial orientation, knowledge management, dynamic capabilities towards e-commerce adoption of SMEs in Indonesia. Journal of Science and Technology Policy Management. |
|
|
Patton P (1998). IQ Emotional Intelligence is the road to happiness and well-being. Jakarta: Media Partners. P 168. |
|
|
Permana H, Harahap F, Astuti B (2016). The Relationship Between Self-Efficacy and Anxiety in Facing Exams in Class IX Students at MTS Al Hikmah Brebes. Journal of Islamic Counseling and Da'wah Guidance 13(2):51-68. |
|
|
Prakoso (1996). How to deliver learning outcomes to improve student cell efficacy. Journal of Psychology 2:11-22. |
|
|
Rainie L, Anderson J (2017). The Future of Jobs and Jobs Training. Pew Research Center. |
|
|
Rintala H, Nokelainen P (2020). Vocational education and learners' experienced workplace curriculum. Vocations and Learning 13(1):113-130. |
|
|
Suhartini (2011). Analysis of Factors Affecting Motives for Online Shopping in Kaskus Community Semarang. Thesis. Management Studies Program. University Diponegoro. Semarang. |
|
|
Suryana (2001). Kewirausahaan, Penerbit Salemba Empat, Jakarta. |
|
|
Suryana (2003) Kewirausahaan, Salemba Empat, Jakarta. |
|
|
Waspada I (2004). Sukses Wirausaha Sukses Profit. Media Komunikasi dan Informasi Pengabdian Masyarakat Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia P 4. |
|
|
Winardi J (2003). Entrepreneur and Entrepreneurship, Kencana, Jakarta. |
|
|
Winarto H (2011). Towards Success Together. Economics Scientific Magazine 14(1):1-38. |
|
|
Wulandari G, Muafi M (2021). The effect of self-efficacy and organizational citizenship behavior toward knowledge sharing: The mediation role of abusive supervision. International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science 10(4):128-138. |
|
|
Yoto (2016). Vocational education development strategy to improve quality of human resources in dealing with Asean Economic Community. In AIP Conference Proceedings 1778(1):030047. AIP Publishing LLC. |
|
|
Yulianingsih IPS, Jaryanto (2013). Relationship of Entrepreneurship Knowledge and Perception of Job Opportunities in Accounting with Entrepreneurial Interest. Journal of Economic Education 2(1):131-145. |
|
Copyright © 2024 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article.
This article is published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0