Full Length Research Paper
Abstract
The chemical composition and seasonal variation of essential oils (EO) extracted from the aerial parts of the traditional medicinal plant Piper rivinoides were analyzed using gas chromatography (GC) coupled with mass spectrometry (MS) and GC coupled with flame ionization detector (GC-FID) technique, respectively. The wild plants were collected from two different sites in the Atlantic Forest. The analysis allowed us to identify 96.60 to 99.80% of the EO composition. The major compounds with the highest relative percentage for both specimens, regardless of the season, were the bioactive monoterpenes α-pinene and β-pinene, which ranged from 34.78 (summer) to 53.87% (winter) and from 15.24% (autumn) to 47.71% (winter), respectively. The seasonal stability of the major compounds in the two study specimens throughout the year indicates that the phenological cycle influences biosynthesis more than abiotic factors. This type of chemical phenotypic stability is rarely observed in species belonging to the Piperaceae family, which is characterized by high chemical variability. Furthermore, this stability is favorable, and P. rivinoides has the potential to be a source of bioactive compounds.
Key words: 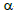 -pinene,
-pinene, 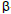 -pinene, Atlantic Forest, aromatic plant, volatile compounds.
-pinene, Atlantic Forest, aromatic plant, volatile compounds.
Copyright © 2024 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article.
This article is published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0