ABSTRACT
This study describes the effect of leadership on job satisfaction, motivation and performance of employees. This study is carried out in Amik Yapennas Kendari. Population for the research consists of all employees of AMIK Yapennas totaling 68 employees. Research method uses a survey approach. The sampling technique is a census with the unit of analysis being the employees at AMIK Yapennas. Analysis tool used to test the hypotheses is the Partial Least Squares (PLS) method. Results showed that leadership has a significant effect on job satisfaction, motivation and performance of employees. Furthermore, job satisfaction and work motivation influence employees’ performance. However, job satisfaction has no significant effect on work motivation. Finally, research proved that motivation and job satisfaction acted as mediating factors to the relationship between leadership and employees’ performance. In this study, the use of job satisfaction and work motivation mediated the relationship between leadership and employees’ performance. The aforementioned outcome has not been studied previously.
Key words: Leadership, job satisfaction, motivation, employees’ performance.
Facing globalization, the human resources (HR) function plays a very dominant role in the activities of organizations, either public or private and nationally and internationally. Parallel to the aforementioned, the increasing competition in the education sector requires that the management of institutions be proactive and able to provide quality education services to the users in order to survive and develop. However, the way is to understand the needs of learners’ perceptions about science, and apply appropriate methods of global needs. Human resource management must motivate the institution and in this case employees are required to carry out the tasks assigned to them in a professional, hard-working, disciplined, honest, loyal, and dedicated to achieve maximum employee performance. Use of proper leadership of superiors is one factor that can drive, steer, guide and motivate employees to perform better at work (Anderson, 1990). Leaders can affect morale, motivation, job satisfaction, security, quality of working life and especially the level of achievement of an organization Organizations generally believed that to achieve excellence, one should seek the maximum possible individual performance, because it is essentially individual performance that affects the performance of the team or work group and ultimately ends up in the level of overall organizational performance. Good performance requires employees to behave as expected by the organization.
This is also reflected in the scope of AMIK Yapennas Kendari. Educational institutions’ function, in human life, is to make people qualified, in the sense that humans have the skills, intelligence and behavior that can give good influence in society and can even change the state of society into a better direction. Thus, Kendari Yapennas AMIK’s duties as principal is to create a human resource (HR) function considering various aspects of a successful man including skilled, competent, competitive, and based on the future needs of human resources as a form of participating in the life of the nation and participating in the establishment of world order. In realizing the aforementioned, AMIK Yapennas should have maximum performance whereby the performance of the organization's resources are key achievement of the objectives of the organization.
This research was done with the consideration that the outcomes achieved at the institution studied, are in the form of the creation of a new generation of competitive human resources, accountable and competitive, so that every employee is required to be professional in carrying out his/her duty. This study aims to test an independent factor affecting employees’ performance at AMIK Yapennas, namely leadership. Allegedly an independent factor that positively affects employees’ performance, in the sense of having good leadership in AMIK Yapennas will be better for increasing job satisfaction, motivation and performance of employees.
This study examines and analyzes the effect of leadership on job satisfaction and work motivation and employees’ performance at AMIK Yapennas Kendari. Technically may be demonstrated through the analysis of structural equation models or structural equation modeling (SEM) based on the theories and concepts of programming packages such as Partial Least Squares (Smart PLS). The job satisfaction variables and the work motivation intervening variables used in this study are chosen because it is expected that these affect indirectly the leadership factor which is anexogenous variable and also affected employees’ performance variables that are endogenous variables.
Leadership
Leadership is a process of influencing others to achieve certain goals (Winandi, 2002, p. 47; Hughes, 1993; Robbins, 1998: 163; Yukl, 2005: 8). A business manager is a leader when she is able to influence subordinates, peers or even their superiors to direct their efforts to the achievement of organizational goals. Miftah Thoha in his book Organizational Behavior (Thoha, 1983: 255) contends that a leader is someone who has the ability to lead, meaning that it has the ability to influence other people or groups without regard to the form of the reason.
Bogardus (1934: 33) defines leadership, in the sense of a leader, as a person who has the skills and strengths in particular skills and strengths in one field, so he is able to influence others to jointly carry out certain activities, for the achievement of one or more goals. Most of the leadership definitions have a common keyword in the definition namely, "a process of influence." Different terms of "who is using the influence, the purpose of influencing efforts, ways to use" lead to describe a leader’s influence. That difference measures direction, relationships, influence, control and exemplary leadership.
Job satisfaction
Job satisfaction concerns every employee individually at work. Job satisfaction is a summative assessment, a feeling or attitude of a person or an employee towards work and has direct relationship with the working environment, type of work, compensation, social relations at work, and others. Job satisfaction is about the fulfillment of some desires and needs through activities or work. Experts define job satisfaction as an attitude and a general feeling of a worker towards work (Davis and Newstroom, 2001:103; Robbins, 1998: 184).
Hasibuan (2008) states that a person tends to pitch if he can achieve job satisfaction. Further, satisfaction is a key driver of morale, discipline, and work performance of employees in supporting the realization of organizational goals.
Work motivation
Motivation grows out of the attitude an employee undertakes when facing a situation at work. Motivation is a condition that drives self-directed employees to achieve corporate goals (Winandi, 2002: 1; Robbins, 1998: 198). Work motivation is one important determinant for the achievement of individuals in an organization. The impact of employee motivation is manifested in the creation of employee morale so that his productivity will increase.
Motivation is a driving force that exists in individuals to do something as good as possible. If these individuals have high motivation then they will be superior performers and help to achieve organizational objectives effectively. Thus, the starting point is the individual motivation because motivation is personal.
Employees’ performance
Employees’ performance can be interpreted as an employee’s work performance which results in quality and quantity of work achieved in performing duties in accordance with the responsibilities given to him (Gibson et al., 1997). Theoretically, the factors that affect achievement of the performance are the capability (ability) and motivation factors, the ability to determine knowledge and skills. Meanwhile, motivation results from an attitude (attitude) in a situation at work (Mangkunagara, 2004: 79).
According to Sutrisno (2010: 150), performance is a record of the results obtained from certain job functions for a certain period. Hasibuan (2008: 105) contends that employees’ performance is achieved by executing the tasks assigned to them based on skills, experience, sincerity and timely. Furthermore, according to Mangkunagara (2002: 67), performance is "The quality and quantity of work accomplished by an employee in performing his duties based on assigned responsibilities". Based on the above definitions, it can be concluded that systematically employees’ performance is a manifestation of the work of employees in terms of quantity, quality and time efficiency in accordance with assigned responsibilities and ability and job description. Employees’ performance is individual and related to his/her personality, and its potential contribution leads to the achievement of one or more specific goals. According to Flippo and Masud (1995), indicators of performance assessment are quality, quantity, timeliness, supervision and responsibility. The population in this study includes all employees of AMIK Yapennas totaling 68 people who were chosen using census method. The research questions of this study are:
(1) Does leadership affect the performance of an employee?
(2) Does leadership affect job satisfaction?
(3) Does leadership affect motivation for work?
(4) Does job satisfaction influence work motivation?
(5) Does job satisfaction affect the performance of employees?
(6) Does work motivation influence employees’ performance?
(7) Does job satisfaction act as a mediating factor on the relationship between leadership and employees’ performance?
(8) Does work motivation act as a mediating factor on the relationship between leadership and employees’ performance?
The purpose of this study is to examine and explain the effect of leadership on job satisfaction, motivation and performance of employees. Also, this study aims to test and explain job satisfaction and motivation as mediating variables between leadership and employees’ performance. The results of this study are expected to be given consideration for Kendari Yapennas AMIK management in policy making, decisions, and program development. Based on the research model shown in Figure 1, the hypotheses in this study are as follows:
H1: Leadership has significant effect on job satisfaction.
H2: Leadership has significant effect on work motivation
H3: Leadership has significant effect on employees’ performance.
H4: Job satisfaction has significant effect on work
motivation.
H5: Job satisfaction has significant effect on employees’ performance
H6: Work motivation has significant effect on employees’ motivation. performance.
H7: Job satisfaction has a role as mediating factor on the relationship between leadership and employees’ performance
H8: Work motivation has a role as mediating factor on the relationship between leadership and employees’ performance.
This study uses a survey approach whereby the sampling technique is a census with the unit of analysis being the employees of AMIK Yapennas. Analysis tool used to test the hypotheses is partial least square (PLS). The research variables, namely: leadership (X) is an exogenous variable; job satisfaction (Y1) and motivation (Y2) are intervening variables, and employee performance (Y3) is an endogenous variable.
Validity test
Validity test is used to measure whether a questionnaire is legitimate or valid. A questionnaire is considered valid if the questions are able to uncover something that will be measured by the questionnaire (Ghozali, 20116: 45). Analysis of data was performed using the Statistical Product and Service Solutions, SPSS version 16.0,an IBM software (Hejase and Hejase, 2013, p. 58). Validity tests were conducted by correlating individual scores of items with their total score. In this case, if the correlation coefficients significance values are less than 5% (level of significance), these indicate that these items are valid.
Test reliability
“Reliability is the degree to which there is an absence of measurement error” (Burns and Burns, 2008: 413). A questionnaire is said to be reliable if the answer to the question is consistent or stable over time (Ghozali, 2011: 45). Reliability test shows the consistency and stability of the scores of a measuring instrument. Reliability testing is only done on the questions considered valid. Testing reliability in this study is conducted using Cronbach’s alpha. According to Hejase and Hejase (2013: 570), “the generally agreed upon lower limit for Cronbach’s alpha is 0.70, although it may decrease to 0.60 in exploratory research”. In addition, when Cronbach`s alpha gets closer to 1, it indicates the higher internal reliability consistency.
Analysis of partial least square (PLS)
PLS is a powerful analytical method because it does not have to assume a certain type of data measurement, can
be applied to all scales of the data, and does not require a lot of assumptions and sample sizes are defined, then uses the help of Smart PLS program (Ghozali, 2011). Evaluation of the outer model is also needed to determine the feasibility of the model. This test consists of testing validity and reliability. Test validity can be seen from the loading factor, discriminant validity (using a square root of average variance extracted / AVE), while reliability can be determined from the composite reliability, Cronbach's alpha, and communality and redundancy.
Path coefficients and hypotheses testing
Hypotheses testing and line coefficients show the direct influence between variables. Path coefficients and the critical point (t-statistics) are presented in Figure 2.
Hypotheses testing results
Table 1 shows that the results of testing the direct influence of leadership on job satisfaction, motivation and employees’ performance can be evidenced by the value of the line coefficient with the positive direction. Positive line coefficient means that the relationship between the leadership and job satisfaction, motivation and performance is unidirectional and is statistically significant since the probability value p-value <α (α = 0.05). Hypotheses testing results show that the relations between leadership and job satisfaction, and leadership and work motivation are positive, strong and statistically significant. This means that a unidirectional increase in leadership leads to increased job satisfaction and work motivation and consequently employees’ performance improvement. So, the hypotheses proposed in this study are accepted or supported by the facts. Moreover, the result of testing the direct influence of job satisfaction on work motivation is estimated by the value of line coefficient of 0.151 as compared with the value of the critical point (t-statistic) of 1.261 which has a probability value (p-value) of 0.212> α = 0.05. This result rejects the relationship between job satisfaction and work motivation. Therefore, hypothesis H4 proposed in this study is rejected or not accepted.
Table 2 shows the results of testing the effect of indirect (mediation) effect to assess the impact of intervening variables in the model. The indirect effect of leadership variable (X) on the variable employees’ performance (Y3) through job satisfaction variables (Y1) is manifested by the value of the line coefficient, 0.587. A value of 0.587 means that effective leadership can lead to good job satisfaction and can improve employees’ performance in AMIK Yapennas by 58.7%. This means that job satisfaction supported the mediation effect between the variables of leadership on employees’ performance. The indirect effect of leadership variable (X) to variable employees’ performance (Y3) through work motivation variable (Y2) manifested by the value of the line coefficient of 0.296. A value of 0.296 means that leadership having a significant effect on employee performance mediated by motivation can trigger increased employee performance at Yapennas Kendari AMIK institutions by 29.6%. This also means that work motivation proved to mediate between leadership and employees’ performance.
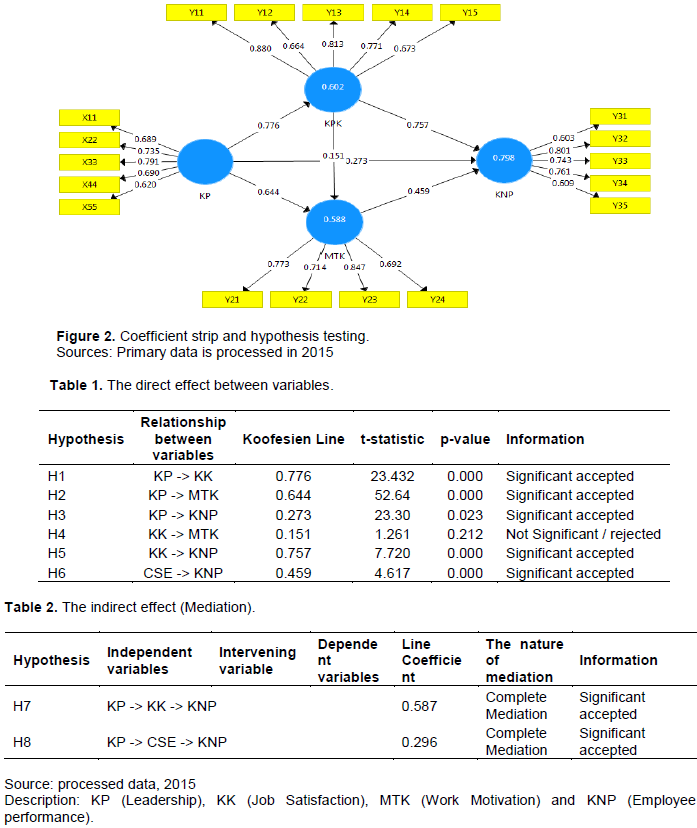
Further in-depth analysis of the relations between leadership, job satisfaction, motivation and performance of employees in this study enriches efforts to see whether or not respondents assess the role of job satisfaction and motivation mediated by leadership influence employees’ performance at AMIK Yapennas dilingkup institutions. Thus, discussions include: the value of the average (mean), the measurement model (outer loading), the discussion of the path coefficients, and hypotheses of testing results.
Influence of leadership on employees’ performance
Employees’ performance review in this study focuses on the level of achievement of the totality of the work. Reported literature forms the basis for assessing and measuring the performance concept in this research. For example, Moeheriono (2009) defined performance as an overview of the level of achievement of the implementation of a program of activities or policies in realizing the goals, objectives, vision and mission of the organization that poured through strategic planning of an organization. Mangkunagara (2002) suggested that employee's performance can be interpreted as an employees’ work performance which results in quality and quantity of work achieved by a workforce in
performing their duties in accordance with the responsibilities assigned to him.
Hypothesis testing results showed that leadership effects on performance can be evidenced by the estimated value of the path coefficient which showed a positive and statistically significant impact. That is, the better the model of leadership applied, the performance of employees will increase. This research was supported by previous researchers, Marpaung (2014), Mihalcea (2013) and Nungky (2013), who provided empirical evidence that leadership has a significant effect on employees’ performance.
Influence of leadership on job satisfaction
The importance of leadership to job satisfaction assessment was based on the opinions expressed by who contended that job satisfaction is always related to the attitude of workers on the job. The attitude took place in cognitive and behavioral aspects. The cognitive aspect of job satisfaction is the trust of workers on the job and the job situation. On the job worker behavior tendency is observed when the job is done, when employees continue to survive in his position, or when the employee works regularly and is disciplined.
Results of testing the effect of leadership on job satisfaction can be evidenced by the value of the path coefficient estimate which showed a positive and statistically significant impact. The test results show that the better the leadership model is applied, the higher the job satisfaction of employees in Kendari Yapennas AMIK institutions. This research was supported by the results of research conducted by Challagalla and Shervani (1996), Shahab and Nisa (2014), and Mihalcea (2013) who stated that leadership has a significant effect on job satisfaction.
Influence of leadership on motivation
Motivation in this research is reflected through employees’ feedback, task orientation, utilization of time, trusting the leader, and awards. Winandi (2002) and Robbins (1998) stated that motivation is self-motivation that drives individual employee to achieve organizational goals. As for leadership, it was referred to, in the field, based on several indicators including direction, relationships, influence, control and exemplary. Some of the respondents have mentioned both concepts (motivation and leadership) from the application point of view. Results assessed by respondents showed that leadership is described most by one indicator namely direction which had the highest average scores followed by other indicators like influence, exemplary, control and relationships. However, based on the results of testing the value of the loading estimate, the biggest contribution to leadership is the indicator of influence.
Results of the strength of the path coefficient for the relationship between leadership influence and work motivation show a positive and statistically significant impact. Therefore, the better the leadership model applied then the higher the motivation of employees working in the sphere of Yapennas AMIK institutions. This research was supported by the results obtained by Sefudin and Mas'ud (2011), Handayani (2010), and Webb (2007) who found that leadership has a major role and a significant effect on work motivation.
Influence of job satisfaction on work motivation
Job satisfaction is the response of employees towards their work and the work environment or the general attitude of an employee to work as measured through five indicators, namely: supervision, type of work, promotion, co-workers, and compensation (Hasibuan, 2008). Motivation referred to in this research is reflected through employees’ feedback, task orientation, utilization of time, trusting the leader, and awards (Winandi, 2002).
Results showing the direct influence of work motivation on job satisfaction is evidenced by the estimate value of line coefficients having a positive influence; however it is not statistically significant (p-value> α = 5%). This means that the increase in job satisfaction variables reflected by indicators supervision, type of work, promotion, co-workers, and compensation does not have influence to increase work motivation. This is supported by previous studies by Laily (2008) who found that job satisfaction does not have a significant effect on employees’ motivation though job satisfaction has a significant effect on the performance of employees at the managerial level. Ostroff (1992) also found that there is a positive relationship between the work environment, job satisfaction, motivation and performance of employees. Thus, measurements of job satisfaction variables do not show influence with work motivation, consequently high and low levels of job satisfaction in employees of AMIK Yapennas have no impact on employees’ motivation.
Influence of employees’ job satisfaction on performance
Job satisfaction in this research is the response of employees to their work and the work environment or the general attitude of an employee towards work that is reflected through the indicators supervision, type of work, promotion, co-workers, and compensation. While the performance of employees in this study focused on the level of achievement of the totality of the job. Reported theories form the basis for assessing and measuring the performance concept in this research. Moeheriono (2009) contends that performance is an overview of the level of achievement of the implementation of a program of activities or policies in realizing the goals, objectives, vision and mission of the organization that are manifested through the strategic planning of the organization. Gibson et al. (1997) suggest that performance can be interpreted as an employee’s work performance which results in quality and quantity of work. Performance may be achieved by a workforce in performing their duties in accordance with the responsibilities assigned.
Results of the hypothesis testing the influence of job satisfaction on performance is evidenced by the estimated value of the path coefficient which showed a positive and statistically significant impact of job satisfaction on employees’ performance. This means that a higher job satisfaction of employees in AMIK Yapennas leads to a higher level of employees’ performance. This means that with better employees’ satisfaction, the performance of employees will increase. The study reinforces previous research results by Sefudin and Mas'ud (2011) and Mihalcea (2014), which state that job satisfaction significantly affects employees’ performance.
Influence of work motivation on employees’ performance
Motivation in this research is manifested through employees’ feedback by four measurement indicators, namely: task orientation, utilization of time, trusting the leader, and awards. Winandi (2002) and Robbins (1998) stated that individual motivation is motivation that drives organizational goals of the organization. The hypothesis test results show that the work motivation influence on the performance can be evidenced by the estimated value of the path coefficient which is positive and statistically significant. This means that with better work motivation, the more the employees’ performance will increase. This result was supported by other researchers, Handayani (2010), Sefudin and Mas'ud (2011) and Cahyono (2012), who demonstrated that work motivation has significant effect on employees’ performance.
Mediating role of job satisfaction between leadership and employees’ performance
Results of this study support the finding that in the initial model leadership as a mediating variable shows direct, positive and statistically significant effect on job satisfaction and employees’ performance. Similar results were obtained testing the influence of job satisfaction mediating variables in the model, then re-testing leadership directly without involving the mediating variables; this led to the finding that leadership influences employees’ performance through job satisfaction though in a partial mediation. The results showed that leadership can directly affect the performance of employees individually or through job satisfaction. Results of the aforementioned tests provide enough empirical evidence that leadership significantly influences employees’ performance mediated by job satisfaction.
Mediating role of work motivation between leadership and employee performance
Results of this study support the finding that in the initial model the mediating leadership variable shows direct, and statistically significantly influence on employees’ motivation and employees’ performance variables. Similar results were obtained testing the influence of work motivation mediating variable in the model, then re-testing leadership directly without involving the mediating variable leading to the finding that work motivation influences employees’ performance and leadership through perfect mediation. The results showed that leadership can directly affect the performance of employees and similar effect is obtained through work motivation. Results of the afroementioned tests provide enough empirical evidence that leadership significantly influences employees’ performance mediated by work motivation.
Research limitations
Results of this research may not be generalized due to the limited focus on AMIK Yapennas Kendari and not including other organizations in South-east Sulawesi Kususnya in Kendari city. This study examines few measurement variables namely, leadership, job satisfaction, work motivation and employees’ performance of employees at AMIK Yapennas Kendari, and the exogenous construct is leadership. Therefore further research is suggested to assess broader factors that may influence job satisfaction, motivation and performance of employees.
(i) Good leadership can contribute to improving the performance of employees. The results of this research are based on the fact that leadership is reflected through the indicators of influence, while the employee's performance is manifested through quantity indicators. Therefore, in improving the performance of employees through leadership roles, there is an increase of influence with real improvement in the totality of the implementation of the tasks assigned and assessed through supervision, quality, timely, and based on the attitude and responsibility.
(ii) Good leadership can improve job satisfaction. Implementation of good leadership is reflected through direction, relationships, influence, control and role models. The aforementioned relationship plays an important and significant role in the improvement of employees’ satisfaction in the scope of AMIK Yapennas Kendari.
(iii) Good leadership can improve employee motivation. Increasing employees’ work motivation through leadership is reflected through direction, relationships, influence, control and role models. These factors have an important role in the implementation of the model of good and effective leadership so that it can give a real contribution in the increase of employees’ motivation in the scope of AMIK Yapennas Kendari.
(iv) Good job satisfaction increased the motivation towards good work. However, the measurement of job satisfaction reflected through supervision, type of work, promotion, co-workers, and compensation did not lead to a statistically significant relation with work motivation.
(v) Good job satisfaction can improve employees’ performance. Measurement of job satisfaction reflected through supervision, type of work, promotion, co-workers, and compensation have an important influence on the performance of employees in the scope of AMIK Yapennas Kendari. The results of this research note that more job satisfaction is reflected by the supervision, while employees’ performance is reflected by the indicator of quantity.
(vi) Good work motivation can improve employees’ performance. The measurement of work motivation is reflected through task orientation, utilization of time, trusting the leader, and awards. These have an important influence on the performance of employees in the scope of AMIK Yapennas Kendari. The results of this research note that motivation is best manifested by trust, while the performance of employees was more reflected by the
indicator of quantity. Furthermore, empirical evidence provided by respondents show that work motivation is manifested by a co-worker’s support who provides the greatest motivation, while the performance of employees is assessed by quality as a measure of the success of the employment.
(vii) Job satisfaction as mediating the relationship between leadership variable influence on employees’ performance can provide a real contribution to improving the performance of employees. Results of this research show that employees’ performance and leadership are partially mediated by job satisfaction. This means that employee's performance already was directly and significantly affected by the leadership before the mediation of job satisfaction which was also significant.
(viii) Finally, work motivation as a mediating variable to the relationship between the leadership and employees’ performance provide real contribution to improving the performance of employees. Results of research show partial mediation of work motivation on employees’ performance through leadership. That is, real employees’ performance is significantly influenced by the leadership and motivation
(ix) Accuracy and precision of the analysis model sebsar 0, 9669. This means that the diversity of leadership on job satisfaction, motivation and employee performance can be explained by 96, 69% and the remaining 3.31% is explained by other variables.
(1) Employees at AMIK Yapennas Kendari showed that Job satisfaction and work motivation were perceived as good; however, such observation necessitates serious attention and continued development by AMIK Yapennas Kendari in order to improve the professionalism of employees, and make satisfaction and motivation more internalized by the employees.
(2) Leadership as manifested by employees from the institution AMIK Yapennas Kendari has clear influence on employees’ performance. Work and employees’ motivation need attention by Kendari Yapennas AMIK management in order to maintain and improve employees’ performance by always evaluating through briefings, and strengthening the relationship between managers and employees to provide a good influence as well as providing exemplary role model for employees.
(3) AMIK Yapennas Kendari must continue to support the employees who are performing well and for employees whose performance is less, the company needs to provide external as well as internal motivational factors.
The author has not declared any conflict of interests.
REFERENCES
|
Anderson LR (1990). Toward a two-track model of leadership training: Suggestions from self-monitoring theory. Small Group Research 21(2):147-167.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
Bogardus ES (1934). Leaders and leadership.
|
|
|
|
|
Burns RB, Burns RA (2008). Business research methods and statistics using SPSS. Sage.
|
|
|
|
|
Cahyono A (2012). Analisa Pengaruh Kepemimpinan, Motivasi dan Budaya Organisasi Terhadap Kinerja Dosen dan Karyawan di Universitas Pawyatan Daha Kediri (Effect of Leadership, Work Motivation and Organizational Climate Against Employee Performance). Jurnal Ilmu Manajemen Revitalisasi 1(1):283-298.
|
|
|
|
|
Challagalla GN, Shervani TA (1996). Dimensions and types of supervisory control: effects on salesperson performance and satisfaction. Journal of Marketing 60(1):89-105.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Davis K, Newstrom JW (2001). Perilaku Dalam Organisasi, edisi Bahasa Indonesia, Alih Bahasa Agus Dharma, SH, M. Ed.
|
|
|
|
|
Flippo EB, Masud M (1995). Manajemen personalia. Erlangga (Personnel Management.).
|
|
|
|
|
Ghozali I (2011). Application of multivariate analysis with SPSS program. Semarang: Diponegoro University Publishing Agency.
|
|
|
|
|
Gibson JL, Ivancevich JM, Donnely JH, Dharma A (1987). Organisasi: perilaku, struktur, proses. Penerbit Erlangga.
|
|
|
|
|
Handayani A (2010). Analisis pengaruh gaya kepemimpinan dan motivasi kerja terhadap kinerja pegawai pada dinas tenaga kerja propinsi Lampung. Jurnal Ilmiah Administrasi Publik dan Pembangunan 1(1):84-92.
|
|
|
|
|
Hasibuan Malayu SP (2008). Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia. edisi revisi. cetakan kesepuluh. Penerbit: Bumi Aksara, Jakarta.
|
|
|
|
|
Hejase AJ, Hejase HJ (2013). Research methods: A practical approach for business students. Masadir.
|
|
|
|
|
Hughes RL (1993). Leadership: Enhancing the lessons of experience. Richard D. Irwin, Inc., 1333 Burridge Parkway, Burridge, IL 60521.
|
|
|
|
|
Laily N (2008). Influence of Individual Characteristics and Job Characteristics and Organizational Climate on Job Satisfaction and Motivation and Performance Manager Medium Industries, National Fertilizers in Indonesia. Dissertation, Surabaya: Airlangga University Graduate Program.
|
|
|
|
|
Mangkunagara AP (2002). HR Performance Evaluation. Bandung. PT Refika.
|
|
|
|
|
Mangkunagara AP (2004). HR Performance Evaluation. Bandung. PT Refika Aditama.
|
|
|
|
|
Marpaung M (2014). Pengaruh kepemimpinan dan Team work Terhadap kinerja karyawan Di koperasi sekjen kemdikbud senayan Jakarta (Influence of leadership and team work on employee performance in the cooperative secretary general of the Ministry of Education and Culture, Senayan Jakarta). Jurnal Ilmiah WIDYA 1(1):33-40. Available at:
View
|
|
|
|
|
Mihalcea A (2013). The Impact of Leader's Personality on Employees' Job Satisfaction. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 78:90-94.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Mihalcea A (2014). Leadership, personality, job satisfaction and job performance. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 127:443-447.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Moeheriono MS (2009). Pengukuran Kinerja Berbasis Kompetensi, Penerbit (Competency-Based Performance Measurement) Ghalia Indonesia.
|
|
|
|
|
Ostroff C (1992). The relationship between satisfaction, attitudes, and performance: An organizational level analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology 77(6):963.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Nungky DL (2013). Leadership role in improving employee's performance in UPT. Aneka Industri Dan Kerajinan Surabaya E-Journal English Department 1(1):1-7.
|
|
|
|
|
Robbins SP (1998). Organizational behavior: concepts, controversies, applications. Prentice Hall.
|
|
|
|
|
Sefudin A, Mas'ud F (2011). Influence of Leadership, Organizational Communication and Motivation Work to Performance (Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan, Komunikasi Organisasi, dan Motivasi Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Karyawan) Officer (Studies in the National Pension Savings Bank Branch Semarang), JRBI. 12:63-74. Available at:
View
|
|
|
|
|
Soegihartono A (2012). Pengaruh kepemimpinan dan kepuasan kerja terhadap kinerja dengan mediasi komitmen (Influence of Leadership and Job Satisfaction with Mediation Performance against Commitment) (di PT Alam Kayu Sakti Semarang). Jurnal Mitra Ekonomi dan Manajemen Bisnis 3(1):123-140.
|
|
|
|
|
Shahab MA, Nisa I (2014). The influence of leadership and work attitudes toward job satisfaction and performance of employee. International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research 2(5):69-77.
|
|
|
|
|
Sutrisno E (2010). Human Resource Management. Kencana Prenada media Group. Jakarta.
|
|
|
|
|
Thoha M (1983). Perilaku Organisasi; Konsep Dasar dan Aplikasinya, Edisi 1.
|
|
|
|
|
Webb K (2007). Motivating Peak Performance: Leadership Behaviors That Stimulate Employee Motivation And Performance. Christian Higher Education 6:53-71.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Winandi J (2002). Motivation and motivating in Management, Jakarta: Rajawali Press.
|
|
|
|
|
Yukl G (2005). Leadership in Organizations. Fifth edition. Interpreting Budi Supriyanto. Jakarta: PT Gramedia Group Index.
|
|