Full Length Research Paper
ABSTRACT
With the emerging field of social entrepreneurship, academicians have raised several research agendas to give a unitary direction to the theoretical groundings and foundations of this concept. The current review is one such attempt to explore the definition of social entrepreneurship and its linkage to social innovation and disruptive thinking. This review aims to understand students’ perspectives and familiarity towards social entrepreneurship; its effectiveness in bringing social change; and the challenges in this field of study. By adopting a secondary research where recent literature on current topic is explored, this review provides fresh insights into the dimensions of social entrepreneurship. Research papers, books, and published materials on social enterprise, innovation, and disruption are rigorously reviewed and explored to derive valuable conclusions. It is inferred from the study that a successful social venture can make a positive impact and contribution to the society, yet a need to measure its implications has been recognized. The research on social entrepreneurship is not united and convergent and requires more in-depth investigations and concrete evidences that can assist with its practical implementation.
Key words: Social entrepreneurship, social innovation, disruptive thinking.
INTRODUCTION
Entrepreneurship is one of the most prominent and essential dimensions that drives economic growth of a nation through increased employment and revenue generation or GDP. The presence and importance of entrepreneurship is common across all developed countries, where economic development and infrastructure are facilitated through the progress of entrepreneurship (Kickul and Lyons, 2016). This importance is realized by several governments who encourage and promote the augmentation of entrepreneurship via various growth strategies, initiatives, and providence of resources to the entrepreneurs and startups. Since its inception, entrepreneurship in the economic context has been considered has business with risks and uncertainties (Groot and Dankbaar, 2014). It is of different types including small business, scalable startup, large company, and social, where social entrepreneurship is one which is unique and less explored. Social entrepreneurship differs from the other types due to the difference in its objectives as it emphasizes on not only enterprise/business development, but also the development of people, society, and environment (Chou, 2018). Social entrepreneurship is most often used with social work, where the difference between NGOs and social services is that social entrepreneurship includes the acquisition of profits. Social entrepreneurship initiates programs or business in a way that helps the poor or deprived section, develops the society, and also gains revenue for a thriving business (Steyaert, and Dey, 2010). It offers innovative products and services that are available to all sections in a society and also benefits the environmental causes. As stated by Thompson et al. (2017), “a high-impact social venture focuses on its mission to “change the world”. For achieving the goals of social entrepreneurship, it is imperative to infuse the enterprise with innovation.
A social venture often requires new methods and means to create inventive products and services that are sustainable and benefits all stakeholders. Innovation, in this context, is referred as social innovation, which is focused on creating services or products that are able to best serve the users and people. Social innovation is a crucial part of social entrepreneurship where it is used to analyze and develop practices that meet the dynamic market needs and solves problems of social environment (Mosher-Williams, 2006). Social entrepreneurship, a relatively less explored area that has piqued interest of several research scholars, emphasizes on conducting business while solving social problems and assisting in the development of the society towards a progressive path. Social entrepreneurship can also be radical, innovative and disruptive. This review paper covers how innovation and disruptive thinking affects social entrepreneurship. The difference in social entrepreneurship thinking with that of entrepreneurship was explored. The more focus was on how social entrepreneurs identify opportunities and apply innovative approaches to tackle social issues. Further, the effectiveness of their methods and ideas on transforming society or bringing progressive changes and the challenges encountered by social entrepreneurs was also studied in this paper.
Disruptive thinking is another key concept that has gained attention in academics and industrial markets in recent years. Disruptive thinking is about “out of the box” thinking; ideologies that challenge the traditional way of doing things.. Disruption in social entrepreneurship can determine how entrepreneurs create new network or market by using disruptive thinking and innovation to disrupt the existing products/services and create new value that brings radical changes in the society and market.
Problem of the study
Social entrepreneurship, a relatively less explored area that has piqued interest of several research scholars, emphasizes on conducting business while solving social problems and assisting in the development of the society towards a progressive path. Social entrepreneurship can also be radical, innovative and disruptive. This review paper covers how innovation and disruptive thinking affect social entrepreneurship. The difference in social entrepreneurship thinking with that of entrepreneurship would be explored while also focusing on how social entrepreneurs identify opportunities in a developed country and apply innovative approaches to tackle social issues. Further, the effectiveness of their methods and ideas on transforming society or bringing progressive changes will be studied. The challenges encountered by social entrepreneurs are also studied in this paper.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Defining Social Entrepreneurship and Social Innovation
Jilinskaya-Pandey and Wade (2019) defined social entrepreneurship as an entity that inculcates diverse and innovative business models to achieve the social and environmental aims of the enterprise. Social entrepreneurship is gaining recognition and popularity in different fields of education, support services, medical industry, and social finance. Social finance that seeks social returns on business investment is a part of social entrepreneurship. These are reasons with profits and financial impact required for the growth of social ventures. There has been an increase in the number of ventures embarked on the foundation of social causes, and the organizations and government are promoting such activities by providing those resources and financial aid (Tiwari et al., 2017). Social entrepreneurs realize the need to developing products and making profits, and also on how to give back to the society. Social entrepreneurship based on a social, environmental or community objectives has increased over time where people are more indulging into this concept. In nations such as the United States of America (USA) and Australia, 11 percent of the businesses are social enterprises (Friedman, 2016).While the growth rate is not high, it is gradually being accepted by the people and communities due to the realization of positive impacts of social ventures on the society as a whole.
Social entrepreneurs thrive for positive changes in the society; while the term “Social innovation refers to innovative activities and services that are motivated by the goal of meeting a social need and that are predominantly diffused through organizations whose primary purposes are social” as defined by Geoff Mulgan in this study in 2006. Jilinskaya-Pandey and Wade (2019) define social entrepreneurship as an entity that inculcates diverse and innovative business models to achieve the social and environmental aims of the enterprise. Social entrepreneurship is gaining recognition and popularity in different fields of education, support services, medical industry, and social finance. Social finance that seeks social returns on business investment is a part of social entrepreneurship. There has been an increase in the number of ventures embarked on the foundation of social causes, and organizations and government are promoting such activities by providing them resources and financial aid (Tiwari et al., 2017). Social entrepreneurs realize the need to developing products and making profits, and also on how to give back to the society. Social entrepreneurship based on a social, environmental or community objective has increased overtime where people are indulging more into this concept. In nations such as U.S. and Australia, 11% of the businesses are social enterprises (Friedman, 2016). While the growth rate is not high, it is gradually being accepted by people and communities due to the realization of positive impacts of social ventures on the society as a whole.
Social entrepreneurs thrive for positive changes in the society, and while the term, social entrepreneur, is new, its concept has been there in the society since the 1980s (Pontus and Ulrika, 2010). Social entrepreneurship has acquired practical relevance in the 80s and 70s, but it is only in the 1990s that the government and research community started to show interest in it. It is acknowledged as a type of business that considers the creation of social wealth and not economic wealth as its major business goal. Due to the increase in social and environment problems plaguing the society, the ideology and perspective of social entrepreneurship has gained high popularity and importance (Pontus and Ulrika, 2010). It is often related to corporate social responsibility and corporate social innovation. According to Gandhi and Raina (2018), social entrepreneurship is implemented by employing innovation to produce social value. Cunha et al. (2015) strengthened the definition of social innovation by determining that it is a concept where ‘change’ is the foundation. It facilitates social change by visualizing a reality and creating it by bringing together resources. Social innovation gives rise to creative ideas and this in the context of social entrepreneurship assists in creating something new that forms the different stages in the complete social entrepreneurial process.
Understanding Social Entrepreneurship: Student perspective
Eppler (2012) determined that a student who is interested in social change can adopt the ideologies of social entrepreneurship or convey their perspectives towards driving social change to their parents, teachers or adults. Calling oneself as social entrepreneur signals that the individual shares beliefs and values to those who target social changes. Waghid and Oliver (2017) reveal from their study that education towards social entrepreneurship increases the interest and desirability of students to launch their own new ventures that can develop their society and economy. Awareness and knowledge towards the concept of social entrepreneurship is thereby very important in affecting the perspectives of youngsters and students. According to Richomme-Huet and De Freyman (2011), there exists few education and training programs that assist students who are motivated towards bringing social changes and embarking on the journey to launch their sustainable enterprise. However, most students are not familiar with the terminology and the importance or relevance of social entrepreneurship. Waghid and Oliver (2017) strengthen this argument that social entrepreneurship education is crucial for the society as it has an eminent role in job creation and poverty reduction. The higher educational institutes must include teachings on social entrepreneurship, which focuses on bringing social change, so as to enhance the knowledge bracket of the students. Obembe et al. (2014) assert that the perspectives of the students towards social entrepreneurship are reliant on their immediate social and cultural environment. The major factors that affect the perspectives of students are capital, university education, survival and familiarity. Students initially gain knowledge from different sources in their early childhood, and apart from school-based literacy, education on social entrepreneurship can also be offered through the film and entertainment industry. It is inferred from this review that the government must give more emphasis on promoting social entrepreneurship education.
Role of Disruptive Thinking
Disruptive thinking and social innovation are key indicators of social entrepreneurship. Social innovation is driven by social entrepreneurs; it gives new perspective to innovation as it helps in designing strategies that can overcome the challenges of post-modern society. As defined by Andrew et al. (2010), “social innovation is a process initiated by social actors to respond to a desire, a need, to find a solution or to seize an opportunity of action to change social relations, to transform a frame or propose new cultural orientations to improve the quality and community living conditions.” Disruptive thinking is also another element that gives more in-depth meaning to social entrepreneurship. Disruptive technologies change the functioning of industries and markets, and the use of disruptive technology and innovation has monumental consequences on social enterprises in the developing economies (Moon et al., 2016). Disruptive thinking refers to the ability to think towards radical changes while depending on non-conventional methods and developments (von Mutius, 2017). Disruptive thinking, creativity, and inventiveness are essential attributes in shaping social enterprises and sustainability.
According to Cieslik (2018), disruptive thinking and transformation is an essential aspect of social entrepreneurship that differentiates it from the other types of entrepreneurship. Social entrepreneurs are often viewed to be creative and open to disruptive ideas so as to bring strictness and certainty in bringing changes to the society. However, its impact on the effectiveness of the social venture is unknown due to a lack of evidence.
CChallenges and Effectiveness of Social Entrepreneurship
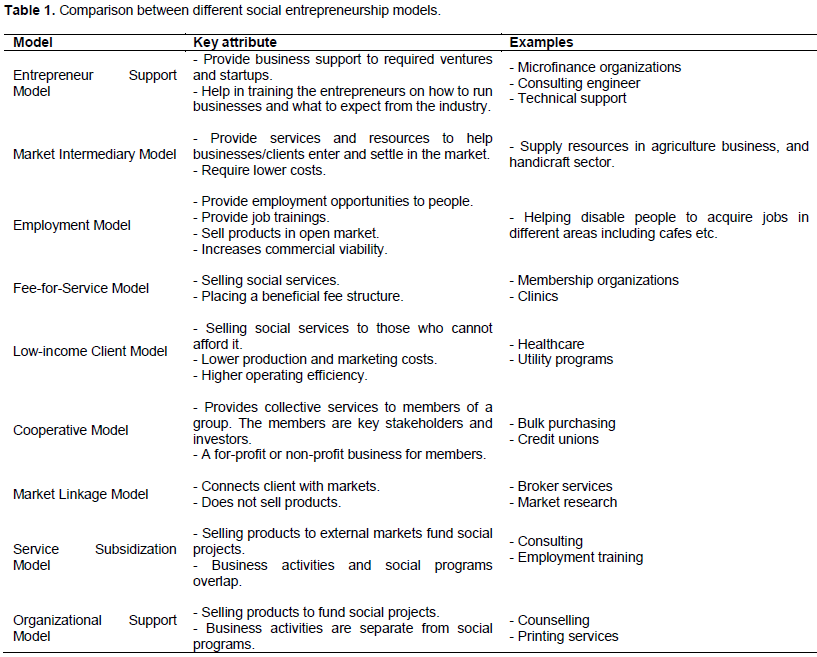
The business models used by social entrepreneurs include social innovative and creativity that assists in bringing positive change in the society. Several social models and applications of social entrepreneurship are (Force, 2017) (Table 1):
1. The Entrepreneur Support Model: Here, the social entrepreneurs provide support to different organizations and consulting services to launch their enterprise.
2. The Market Intermediary Model: This model focuses more on marketing and selling the products or services of other businesses such as small-scale farmers.
3. The Employment Model: The social entrepreneurs provide platforms and different job opportunities to individuals for increasing employability in the society.
4. The Fee-for-Service Model: The social entrepreneurs seek charges from the customer for the socially beneficial services provided by them.
5. The Low-income Client Model: The social entrepreneurs offer services to unprivileged and low-earning businesses or individuals. These can include healthcare programs.
6. The Cooperative Model: Here, the social entrepreneurs provide member services to a group that shares a common need or goal.
7. The Market Linkage Model: The entrepreneurs act as a medium to connect businesses with other businesses such as bringing together clients with Marketing firms.
8. The Service Subsidization Model: Here, the social entrepreneurs fund social programs in different sectors or industries.
Social entrepreneurship, though considered to be effective in helping the society, does not have sufficient evidence to support its effectiveness in bringing social change and resolving social issues. According to a study conducted by Diochon (2013), social entrepreneurship is considered to combat poverty, and yet, there has been no positive impact of social entrepreneurship on the community’s employment and entrepreneurial capacity. Considering the challenges in this field, one challenge of social entrepreneurship is the lack of method to measure the impact made on the people or society. While the profits and revenue generation can be measured, it often becomes difficult to evaluate and precisely measure the social, environmental or sustainable impacts. Without this measurement, it becomes tedious to understand the changes required within the current business model or venture it to ensure better results. Apart from this, the other challenges faced by social entrepreneurs are difficulties in managing diversification, lack of resources, lack of funds, and poor collaboration with other authorities (Zainol et al., 2014).
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This review adopts descriptive methodology where secondary data such as books, research papers, reports and articles are explored to meet the objectives of the study. As the study aims to explore social entrepreneurship and its linkage to social innovation and disruptive innovation and to understand how students perceive social entrepreneurship, 28 articles were reviewed from 2006 to 2019. Articles were selected based on their quality and relevance to the research topic and aim. The study is subjective in nature that utilizes a phenomenon or setting to understand the topic of research. The literature exploration and synthesis are performed as a secondary data collection method by using the computer and electronic databases on web such as Google Scholar, Google Search Engine, academia database, online newsletters, existing thesis on this subject, journal of social entrepreneurship, and other peer reviewed journals. Secondary sources on social entrepreneurship, innovation and disruption are referred; which are as follows:
1. Research papers and books related to the current topic of study.
2. Websites and online published materials on social enterprises and their development.
3. Reports of government bodies and industrial agencies on social entrepreneurship.
4. Web resources on social entrepreneurship and its role in economic development.
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
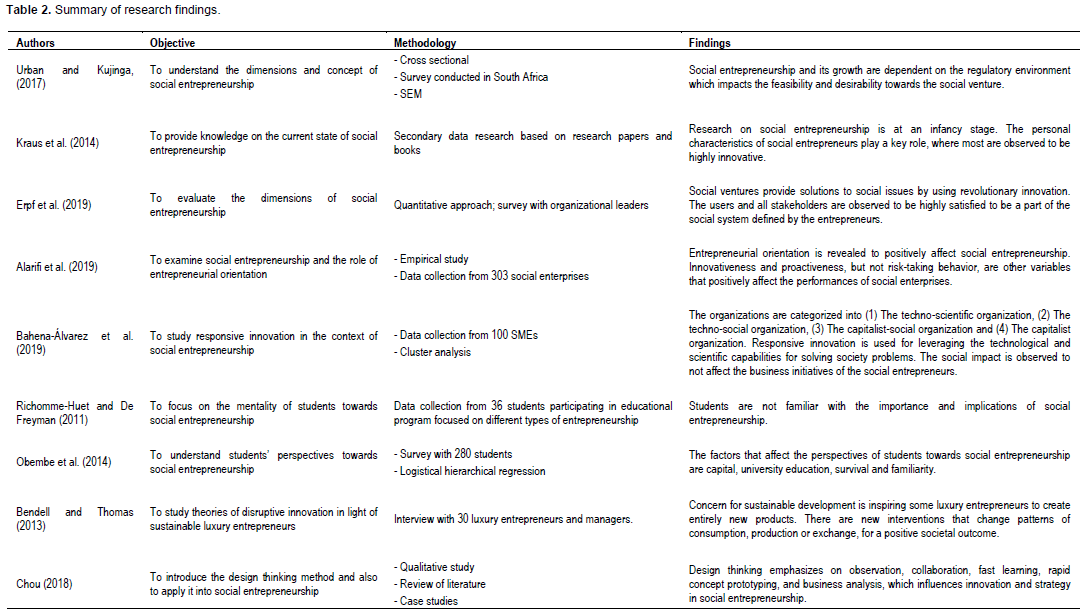
Here, the major inferences are drawn from the existing body of literature so as to reach the conclusion. In this section different studies are discussed, as shown in Table 2.
DISCUSSION
It is evident from the review that there is strong impetus for additional research in this field. There is a need to explore and evaluate the goals and motivation of students and of social enterprises to gain a more in-depth knowledge on the area and also on the practical application of social entrepreneurship. More evidence on the inclusion of social capital in the concept of social entrepreneurship is needed, along with measurement strategies to evaluate the impact of social entrepreneurship on the society. Additional information and empirical investigations in this field will clarify the extent of social entrepreneurship and provide more insights into this field of research.
CONCLUSION
In a nutshell, social entrepreneurship is very crucial topic in today’s world. Universities should start implementing social entrepreneurship in the curriculum in order to increase the awareness on students. Academicians should research more on social entrepreneurship. Disruptive innovation and disruptive thinking are the hallmarks of technology world that if properly implemented can boost the business prospect and profit. The term helps individual or company to come up with different strategic approaches; these two terms, disruptive innovation, are critical elements of the evolution of technology. This can be either positive or negative. However, it is beneficial for the company to come up with rewarding models so that they can be prioritized their choice of design. Most of the social entrepreneurship business suffered significantly due to lack of creativity, lack of finance and fear of risk taking. Personalities and individual behavior can also affect business success. Most of the entrepreneurs start business for profit making but those that focus on social entrepreneurship, they have social mission. Thus, it is very crucial to understand social entrepreneurship in order to solve social issues. Table 3 demonstrates the research gaps and research problems identified from the current review.

The aforementioned research problems are few areas in which further research can be conducted. This review paper can assist the scholars pursuing a similar field of research who can further enrich the body of knowledge through more extensive investigations.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors have not declared any conflict of interests.
REFERENCES
|
Alarifi G, Robson P, Kromidha E (2019). The manifestation of entrepreneurial orientation in the social entrepreneurship context. Journal of Social Entrepreneurship 10(3):307-327. |
|
|
Andrew C, Klein JL, Mohamoud H (2010). Social Innovation: What is it and why is it important to understand it better. Québec: CRISES. Available at: |
|
|
Bahena-Álvarez IL, Cordón-Pozo E, Delgado-Cruz A (2019). Social entrepreneurship in the conduct of responsible innovation: Analysis cluster in Mexican SMEs. Sustainability 11(13):3714. |
|
|
Chou DC (2018). Applying design thinking method to social entrepreneurship project. Computer Standards and Interfaces 55:73-79. |
|
|
Cieslik K (2018). The quandaries of social entrepreneurship studies-a discursive review of the discipline. Review of Social Economy 76(3):352-376. |
|
|
Cunha J, Benneworth P, Oliveira P (2015). Social entrepreneurship and social innovation: A conceptual distinction. In Handbook of research on global competitive advantage through innovation and entrepreneurship pp. 616-639. |
|
|
Diochon M (2013). Social entrepreneurship and effectiveness in poverty alleviation: A case study of a Canadian First Nations community. Journal of Social Entrepreneurship 4(3):302-330. |
|
|
Eppler I (2012). The Problem with "Social Entrepreneurship": A Student's Perspective. Stanford Social Innovation Review. Available at: |
|
|
Erpf P, Ripper MJ, Castignetti M (2019). Understanding Social Entrepreneurship Based on Self-Evaluations of Organizational Leaders-Insights from an International Survey. Journal of Social Entrepreneurship 10(3):288-306. |
|
|
Force AG (2017). 9 Business Model Examples for Social Enterprises. Available at: |
|
|
Friedman L (2016). The Findings of This Massive Global Social Entrepreneurship Study Will Surprise You. Entrepreneur.com. Available at: |
|
|
Gandhi T, Raina R (2018). Social entrepreneurship: the need, relevance, facets and constraints. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research 8(1):1-13. |
|
|
Groot A, Dankbaar B (2014). Does social innovation require social entrepreneurship? Technology Innovation Management Review 4(12):17-26. |
|
|
Jilinskaya-Pandey M, Wade J (2019). Social entrepreneur quotient: An international perspective on social entrepreneur personalities. Journal of Social Entrepreneurship 10(3):265-287. |
|
|
Kicku lJ, Lyons TS (2016). Understanding social entrepreneurship: The relentless pursuit of mission in an ever-changing world. Routledge. |
|
|
Kraus S, Filser M, O'Dwyer M, Shaw E (2014). Social entrepreneurship: an exploratory citation analysis. Review of Managerial Science 8(2):275-292. |
|
|
Moon C, Kavanagh, Jeffrey, Gebbels J, Korsgaard K (2016). Social Entrepreneurship and Disruptive Innovation: Evaluating the use of Rumie's Free Educational Software in Seven Developing Economies. In European Conference on Innovation and Entrepreneurship. Academic Conferences International Limited. P 485. |
|
|
Mosher-Williams R (2006). Research on social entrepreneurship: Understanding and contributing to an emerging field (ARNOVA Occasional Paper Series, Volume 1, Number 3). Indianapolis, Ind.: Association for Research on Nonprofit Organizations and Voluntary Action. |
|
|
Obembe E, Otesile O, Ukpong I (2014). Understanding the students' perspectives towards entrepreneurship. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 145:5-11. |
|
|
Pontus B, Ulrika SH (2010). Social entrepreneurship- a survey of current research. Working Papers Series from Swedish Entrepreneurship Forum. International Review of Entrepreneurship 8(2):71-112. |
|
|
Richomme-Huet K, De Freyman J (2011). What sustainable entrepreneurship looks like: An exploratory study from a student perspective. In: ICSB World Conference Proceedings (1). International Council for Small Business (ICSB). |
|
|
Steyaert C, Dey P (2010). Nine verbs to keep the social entrepreneurship research agenda 'dangerous'. Journal of Social Entrepreneurship 1(2):231-254. |
|
|
Thompson M, Mawson S, Martin F (2017). Disruptive Thinking, Creativity and Social Innovation. Available at: |
|
|
Tiwari P, Bhat AK, Tikoria J (2017). The role of emotional intelligence and self-efficacy on social entrepreneurial attitudes and social entrepreneurial intentions. Journal of Social Entrepreneurship 8(2):165-185. |
|
|
Urban B, Kujinga L (2017). The institutional environment and social entrepreneurship intentions. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior and Research 23(4):638-655. |
|
|
von Mutius B (2017). Disruptive thinking. Das Denken, das der Zukunft gewachsen ist, Offenbach. |
|
|
Waghid Z, Oliver H (2017). Cultivating social entrepreneurial capacities in students through film: Implications for social entrepreneurship education. Educational Research for Social Change 6(2):76-100. |
|
|
Zainol FA, Daud WNW, Abdullah Z, Yaacob MR (2014,). Social Entrepreneurship and Organizational Effectiveness: The way forward to solve Urban Poverty?. In International Conference on Business, Law and Corporate Social Responsibility. pp. 111-116. |
|
Copyright © 2024 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article.
This article is published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0