Full Length Research Paper
ABSTRACT
This study characterized microbial strains isolated from diesel fuel samples collected from the tank of a generating set at the Institute of Research for Development in Pointe-Noire (Congo). Two bacterial isolates (G2 and G3) were distinguished by their color on agar plates and were characterized by their
Key words: Pseudomonas, emulsification index, diesel fuel, gasoline, hexane.
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RESULTS
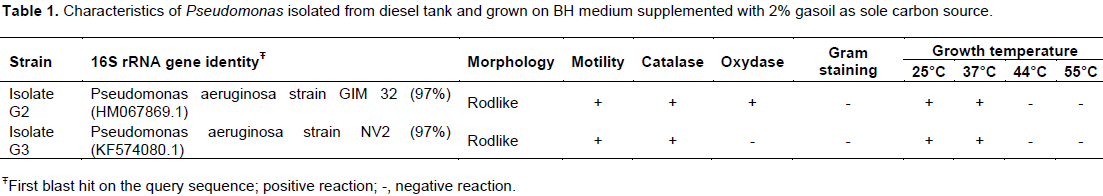
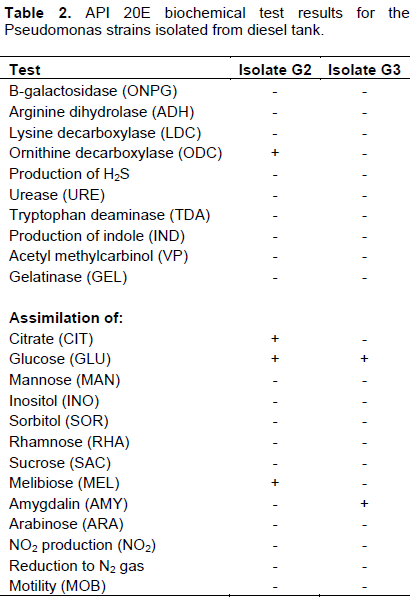
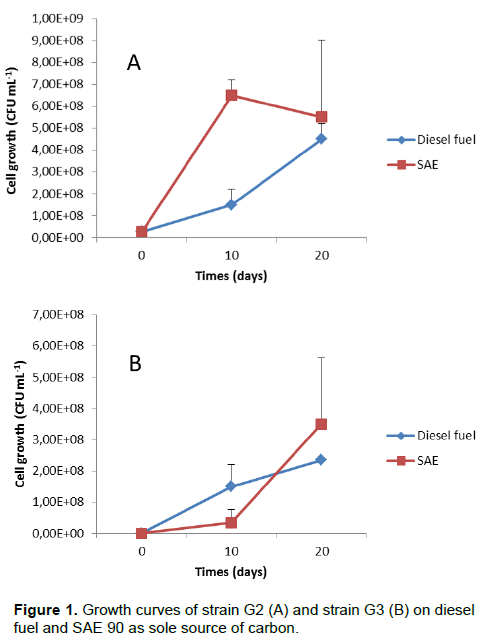
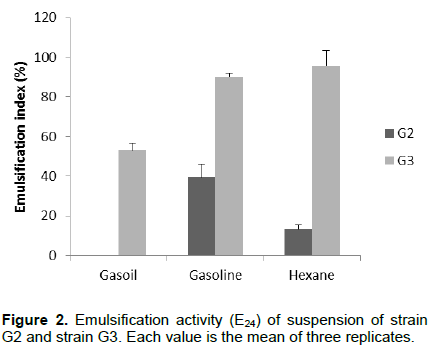
DISCUSSION
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
REFERENCES
|
Abdel-mawgoud AM, Lépine F, Déziel E (2010). Rhamnolipids : diversity of structures , microbial origins and roles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 86:1323-1336 |
|
|
Altschul XF, Stephan J, Thomas L, Madden X, Alejandro A, Schäffer X, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:3382-3402. |
|
|
Arutchelvi J, Doble M (2010). Characterization of glycolipid biosurfactant from Pseudomonas aeruginosa CPCL isolated from petroleum-contaminated soil. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 51:75-82. |
|
|
Atlas RM (1981). Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons: an environmental perspective. Microbiol. Rev. 45(1):180-208. |
|
|
Banat IM, Makkar RS, Comeotra SS (2000). Potential commercial applications of microbial surfactants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 53: 495-508. |
|
|
Banat IM, Satpute SK, Cameotra SS, Patil R, Nyayanit NV (2014). Cost effective technologies and renewable substrates for biosurfactants' production. Front. Microbiol. 5(697):1-18. |
|
|
Bharali P, Konwar BK (2011). Production and physico-chemical characterization of a biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa OBP1 isolated from petroleum sludge. Appl.Biochem.Biotechnol. 164 :1444-1460. |
|
|
Collins Chris (2007). Implementing Phytoremediation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons, Methods in Biotechnology. Humana Pre. Vol. 23. |
|
|
Coutinho JOPA, Silva MPS, Moraes PM, Monteiro AS, Barcelos JCC, Siqueira EP, Santos VL (2013). Bioresource technology demulsifying properties of extracellular products and cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa MSJ isolated from petroleum-contaminated soil. Bioresour. Technol. 128:646-54. |
|
|
Das P, Yang X-P, Ma LZ (2014). Analysis of biosurfactants from industrially viable Pseudomonas strain isolated from crude oil suggests how rhamnolipids congeners affect emulsification property and antimicrobial activity. Front. in Microbiol. 5(696):1-8. |
|
|
Desai DJ, Banat IM (1997). Microbial Production of Surfactants and Their Commercial Potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 61:47-64. |
|
|
Dhamodharan D, Jayapriya J (2016). Integrated approach for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon solubilization from the soil matrix to enhance bioremediation integrated approach for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon solubilization from the soil matrix to enhance bioremediation. Bioremed. J. 19(4):287-295. |
|
|
Dieter H, Rolf H, Reiner C, Kleber H-P (2005). Extracellular microbial lipids as biosurfactants. In cheper W, Belkin Th, Bley S, Bohlmann Th, Doran J, Gu PM, Hu MB, Mattiasson WS, Nielsen B, Seitz J, Ulber H, Zeng R, Zhong AP, Zhou JJ, ed. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology. Springer Berlin Heidelberg pp. 53-93. |
|
|
Dötsch A, Schniederjans M, Khaledi A, Hornischer K, Schulz S, Bielecka A, Eckweiler D, Pohl S, Häussler S (2015). The Pseudomonas aeruginosa transcriptional landscape is shaped by environmental heterogeneity and genetic variation. mBio 6(4):e00749-15. |
|
|
Ferhat S, Mnif S, Badis A, Eddouaouda K, Alouaoui R, Boucherit A, Mhiri N, Moulai-Mostefa N, Sayadi S (2011). Screening and preliminary characterization of biosurfactants produced by Ochrobactrum Sp. 1C and Brevibacterium Sp. 7G isolated from hydrocarbon-contaminated soils. Int. Biodeter. Bioremed. 65:1182-88. |
|
|
Gaylarde CC, Bento FM, Kelley J (1999). Microbial contamiantion of stored hydrocarbon fuels and its control. Rev. de Microbiol. 30:1-10. |
|
|
Gregersen T (1978). Rapid method for distinction of gram-negative from gram-positive bacteria. European J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 5:123-127. |
|
|
Gudina Ej, Pereira JFB, Rodrigues L, Coutinho JAP, Teixeira JA (2012). Isolation and study of microorganisms from oil samples for application in microbial enhanced oil recovery. Int. Biodeter. Bioremed. 68:56-64. |
|
|
Hamed SB, Gam ZBA, Rezgui R, Ghram A, Labat M (2013). Diversity of culturable aerobic bacteria colonizing four petroleum by-products storage reservoirs. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 7(21):2542-2549. |
|
|
Ismail W, Al. Sultanah Shammary, El-sayed WS, Obuekwe C, El Nayal AM, Salam A, Raheem ASA, Al-humam A (2015). Stimulation of rhamnolipid biosurfactants production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa AK6U by organosulfur compounds provided as sulfur sources. Biotechnol. Rep. 7:55-63. |
|
|
Itoh S, Suzuki T (1972). Effect of rhamnolipids on growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mutant Deficient in n-paraffin-utilizing ability. Agric. Biol. Chem. 36:2233-2235. |
|
|
Khire JM (2010). Bacterial biosurfactants, and their role in microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 672:146-57. |
|
|
Kiewitz C, Tümmler B (2000). Sequence diversity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: impact on population structure and genome evolution. J. Bacteriol. 182:3125-3135. |
|
|
Klockgether J, Cramer N, Wiehlmann L, Davenport CF, Tümmler B (2011). Pseudomonas aeruginosa genomic structure and diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2(150):1-18 |
|
|
Klofutar B, Golob J (2007). Microorganisms in diesel and in biodiesel fuels. Acta. Chim. Slov. 54:744-48. |
|
|
Leahy JG, Colwell RR (1990). Microbial degradation of hydrocarbons in the environment. Microbiol. Rev. 54(3): 305-315. |
|
|
Liang L, Song X, Kong J, Shen C, Huang T, Hu Z (2014). Anaerobic biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a facltative anaerobe Pseudomonas Sp. JP1. Biodegr. 25:825-833. |
|
|
Liu H, Liang R, Tao F, Ma C, Liu Y, Liu X, Liu J (2012). Genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain SJTD-1, a bacterium capable of degrading long-chain alkanes and crude oil. J. bacteriol. 194(17):4783-4784. |
|
|
Marchant R, Banat IM (2012). Biosurfactants: a sustainable replacement for chemical surfactants? Biotechnol. Lett. 34:1597-1605. |
|
|
Nie M, Yin X, Ren C, Wang Y, Xu F, Shen Q (2010). Novel rhamnolipid biosurfactants produced by a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain NY3. Biotechnol. Adv. 28(5):635-643. |
|
|
Obayori OS, Salam LB, Ogunwumi OS (2014). Biodegradation of fresh and used engine oils by Pseudomonas. Bioremed. Biodegr. 5(1):1-7. |
|
|
Pacwa-PÅ‚ociniczak M, PÅ‚aza GA, Poliwoda A, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2014). Characterization of hydrocarbon-degrading and biosurfactant-producing Pseudomonas sp. P-1 strain as a potential tool for bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 21:9385-9395. |
|
|
Patel RM, Desai AJ (1997).Biosurfactant production from Pseudomonas aeruginosa GS3. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 25:91-94. |
|
|
Pennings S C, Call BDM, Hooper-Bui L (2014). Effects of oil spills on terrestrial arthropods in coastal wetlands. Bioscience. 64:789-795. |
|
|
Perfumo A, Banat IM, Canganella F, Marchant R (2006). Rhamnolipid production by a novel thermophilic hydrocarbon-degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa AP02-1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 72: 132-138. |
|
|
Pirôllo MPS, Mariano AP, Lovaglio RB, Costa SGVAO, Walter V, Hausmann R, Contiero J (2008). Biosurfactant synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa LBI isolated from a hydrocarbon-contaminated site. J. Appl. Microbiol. 105:1484-1490. |
|
|
Qazi MA, Malik ZA, Qureshi GD, Hameed A, Ahmed S (2013). Yeast extract as the most preferable substrate for optimized biosurfactant production by rhlB gene positive Pseudomonas putida SOL-10 isolat. Bioremed. Biodegr. 4(7):204 |
|
|
Rocha VMP, Mendes JS, Estela M, Giro A, Melo VMM, Rocha L, Gonçalves B (2014). Biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa MSIC02 in cashew apple juice using a 24 full factorial experimental design. Chem. Ind Chem. Eng. Q. 20(1): 49-58. |
|
|
Ron, EZ, Rosenberg E (2002). Biosurfactants and oil bioremediation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 13(3): 249-252. |
|
|
Seeley HW, Vandemark PJ, Lee JJ (1995). Microbes in action, a laboratory manual of microbiology, 4th ed. Freeman WH and Company, New York, NY. |
|
|
Sharma A, Kumar P, Rehman M B (2014). Biodegradation of diesel hydrocarbon in soil by bioaugmentation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a laboratory scale study. Int. J. Environ. Bioremed. Biodegr. 2(4): 202-212. |
|
|
Shen K, Sayeed S, Antalis P, Gladitz J, Ahmed A, Dice B, Janto B, Dopico R, Keefe R, Hayes J, Johnson S, Yu S, Ehrlich N, Jocz J, Kropp L, Wong R, Wadowsky RM, Slifkin M, Preston RA, Erdos G, Post JC, Ehrlich GD, Hu FZ (2006). Extensive genomic plasticity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa revealed by identification and distribution studies of novel genes among clinical isolates. Infect. Immun. 74(9):5272-5283. |
|
|
Silliman BR, de Koppel JV, McCoy MW, Diller J, Kasozi GN, Earl K, Adams PN Zimmerman AR (2012). Degradation and resilience in louisiana salt marshes after the BP–deepwater horizon oil spill. Proceed. Nat. Acad. Sci.109:11234- 11239. |
|
|
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994). Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RG, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds), Methods for General Mol. Bacteriol. 5:611-654. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC. |
|
|
Soberon-Chavez G, Lépine F, Déziel E (2005). Production of rhamnolipids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 68:718-725. |
|
|
De Souza Pereira Silva D, De Lima Cavalcanti D, De Melo JVE, Dos Santos PNF, Da Luz ELP, De Gusmão M, De Fatima Vieira de Queiroz Sousa NB (2015). Bio-removal of diesel oil through a microbial consortium isolated from a polluted environment. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 97:85-89. |
|
|
Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin A L, Mizoguchi SD, Warrener P, Hickey MJ, Brinkman FS, Hufnagle WO, Kowalik DJ, Lagrou M, Garber RL, Goltry L, Tolentino E, Westbrock-Wadman S, Yuan Y, Brody LL, Coulter SN, Folger KR, Kas A, Lar-big K, Lim R, Smith K, Spencer D, Wong GK, Wu Z, Paulsen IT, Reizer J, Saier MH, Hancock RE, Lory S, Olson MV (2000). Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nat. 406:959-964 |
|
|
Tang YW, Ellis NM, Hopkins MK, Smith DH, Dodge DE, Persing DH (1998). Comparison of phenotypic and denotypic techniques for identification of unusual aerobic pathogenic gram-negative Bacilli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36(12):3674-3679 |
|
|
Widada J, Nojiri H, Kasuga K, Yoshida T, Habe H, Omori T (2002). Molecular detection and diversity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria isolated from geographically diverse sites. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 58:202-209. |
|
|
Wongsa P, Tanaka M, Ueno A, Hasanuzzaman M, Yumoto I, Okuyama H (2004). Isolation and characterization of novel strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens possessing high efficiency to degrade gasoline, kerosene, diesel oil, and lubricating oil. Curr. Microbiol. 49:415-422. |
|
|
Yoshida N, Yagi K, Sato D, Watanabe N, Kuroishi T, Nishimoto K, Yanagida A, Katsuragi T, Kanagawa T, Kurane R, Tani Y (2005). Bacterial Communities in Petroleum Oil in Stockpiles. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 99(2):143-149. |
|
Copyright © 2024 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article.
This article is published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0