ABSTRACT
The purpose of the study is to examine the effect of headhunting recruitment strategy on employee retention strategy in the Nigerian banking industry. The objective is to examine the effect of headhunting recruitment strategy on employee retention in the banking industry. The study makes use of primary data by administering structured questionnaire to employees of Zenith Bank Plc, a money deposits bank in Egor local government area, Oredo local government area, and Ikpoba Okha local government area in Benin City of Edo State of Nigeria and Stata 13.0 statistical tool is used for the analysis of data. The results show that headhunting recruitment strategy has a significant positive effect on employee retention strategy while selection practice has a significant positive effect on employee retention strategy.
Keywords: Employee retention strategy, headhunting recruitment strategy, recruitment, selection practices.
The recruitment and selection process is one of the most important human resource management used by banks as it is the point of entry into the banks and also where the banks recruit talents that drive their goals and interest (Walker, 2001). The recruitment of candidates for a position in organizations through headhunting in human resource strategy is critical to the company's success (Deepakshi and Sheetal, 2014:2-3). Smith and Rupp (2004) cited in Deepakshi and Sheetal (2014:2-3), are of the view that the internet has drastically changed the face of recruitment. Employers have to market themselves by instituting a well-implemented e-recruitment program to find better quality candidates to occupy a sensitive position at lower-cost through the recruitment strategy of head-hunting (James and Matthew, 2012).
Headhunting is an external recruitment policy whereby outsourcing organizations have candidates employed elsewhere to suitably fill the business position (Dessler, 2014a). Therefore, the ability to retain talented employees is very keen to the banking industry as the business world is continuously changing into a global market where competition for rare talent is high (Akala, 2012). Meanwhile, the banks need to maximize their performance and sustain competition by adopting headhunting recruitment practices that contribute towards employee retention (Gazzawi and Accoumeh, 2014). Headhunting is a human resource management strategy employed by the management of the banking industry for the process of recruitment and selection of appropriate candidates for various vacant positions (Dessler, 2014b). James and Matthew (2012:19) stated that headhunting is a recruitment and selection process where the recruiters find the contact details of a specific candidate that has some specific skills so as to participate in the recruitment process.
Tsuma (2017) claims that it is the responsibility of the human resource management in the banking industry to recruit and retain the employees through the avenue of headhunting recruitment policies and strategies that retain and increase on-the-job satisfaction for the employees (Das and Baruah, 2013). However, corporate organizations need talented employees with skills for maintaining the sustainable competitive advantage and yearn for career opportunities to develop and grow their level of competence (De Waal and Frijns, 2011:4-19). Employee retention is an obligation to stay with an existing business or corporate organizations on an ongoing basis (Pathak, (2011) cited in Shuku (2015). AL-Qudah et al. (2014) cited in Shuku (2015:1-66) add that retention is the ability to retain capable employees that an organization needs to keep for a longer period than its competitors. Retention strategies employed by banks help to increase job performance (Tsuma, 2017). Moreover, studies had demonstrated that there is a possibility of other factors that enhance retention strategies, beyond the use of headhunting recruitment process, affecting the level of retention strategies experienced by a firm (Trivedi and Muduli, 2015:23-37). Some studies have identified headhunting recruitment and selection practices to have a positive effect on retention strategies while others demonstrate that they have no effect on the levels of retention strategies (Karemu et al., 2014; Dessler, 2007). Based on this premise, the following research questions were raised to guide the study under consideration. Does headhunting recruitment strategy has any effect on employee retention in the banking industry? Does selection practices have any effect on employee retention in the banking industry? In addition, the study would bridge the gap in research by examining whether headhunting recruitment practices would influence employee retention strategies in the banking industry.
The broad objective of this study is to examine the effect of headhunting recruitment strategy on employee retention strategy in Nigeria banking industry. Specifically, the study seeks to:
(i) Examine the effect of headhunting recruitment strategy on employee retention in the banking industry.
(iii) Determine the effect of selection practices on employee retention in the banking industry.
Formulation of research hypotheses
The hypotheses for the study under consideration were formulated in a null form:
HO1: Headhunting recruitment strategy has no significant effect on employee retention strategy.
HO2: Selection practice has no significant effect on employee retention strategy.
Employee retention strategy
Employee retention is the ability and capability of an organization to retain its recruited staff for a long period of time in organizations with good financial incentives (Samuel and Chipunza, 2009). According to Wijesiri, Paranagama, Sirirwardhana, Thilakarathna, Weerarathna, and Pathirana (2019:2), "employee retention is one of the most deliberated concepts in the area of human resource management and highlighting the reasons for employee turnover and implementing the necessary policies to retain employees in a competitive market environment”. Retention is practices adopted in the corporate organization in order to encourage employees to remain for as specified in the contracts agreement (Das and Baruah, 2013). Eisenberger et al. (2002) are of the view that corporate organizations must enact its energy and time in retaining the quality employees that turn the prospect of the organization around for the positive outcome. Cropanzano et al. (2001:164-209), "argue that fair process leads to intellectual and emotional recognition in the mind of the employees thereby creating trust and commitment which build voluntary cooperation in strategy execution". According to Imran et al. (2015: 840-844), "employees are a true asset for any organization and every organization wants to get the maximum benefit from its resources". Akintayo (2010:1-8) is in the view that if employees are well satisfied and develop a high degree of satisfaction with their jobs, they are more likely to be committed to the organization than in the case of those who are not satisfied with their jobs due to the same factors. Zhou et al. (2009) added that compensation provides competitive base salary levels necessary to attract and retain talent and compensates for day-to-day responsibilities performed at a fully acceptable level and above.
Headhunting recruitment strategy
Headhunting is a recruitment strategy aimed at connecting employers to prospective employees (Rathling, 2012). Valkonen et al. (2013) argue that headhunting recruitment strategy is a recruitment model employed to attract the suitable and best candidate for available positions in any organization. Therefore, "recruitment based on the headhunting selection process is built on the premise of recruiting and retaining the right and a quality candidate that enhances the human resource needs of any firm positively (Newell, 2005). It is a process in which capable employees are located and incorporated into the workforce of organizations. The highly competitive nature of today's business world has made it very necessary for businesses to seek the most cost-effective way to recruit new employees as well as for employees to seek employers (Rathling, 2012). Headhunting means the use of one or more strategies to relate intellectual human capital to the organizational vacancies (Sinha and Thaly, 2013). However, many recruitment agents have moved much of their recruitment process online so as to improve the speed by which candidates can be matched with live vacancies, and reduce the cost and time duration of these exercises (Suvankulov et al., 2012).
Selection practices
Dessler (2007) is of the opinion that the selection practice strategy is a process of matching the right people with the right vacant jobs placement. According to Subramaniam et al. (2011: 27-37), employee selection is the process of collecting and evaluating information about an individual in order to extend an offer of employment. Ombui et al. (2012: 19-64) lay credence to the common process adopted by most organizations when carrying out recruitment by relying on ‘a behavior-based interview' which can help to some extent in predicting the subsequent output of employees better than, let say, ‘situational interviews'. Selection practice involves defining vacancies, attracting applicants, assessing candidates and making decisions on the best candidates to fill positions (Beardwell and Wright, 2012). Recruitment and selection are veritable avenue employ by human resource managers and the entire company to hire the right people and retain them (Shuku, 2015:1). Shuku (2015:16) argues that selection strategy is about finding the best source, hiring the best talents and keeping the organization competitive on the job market and retains its best employees.
Ombui et al. (2012) examined how recruitment and selection influence employee performance in research institutes in Kenya. The study population was drawn from all Government-owned research institutes formed under the Science and Technology Act. Cap 250. The target population was drawn from the research institutes that were within Nairobi county and its environs. The study adopted a stratified sampling technique while the sample size was 256 employees. Statistical package for social sciences (SPSS) was used to analyze the quantitative data. The results of the study revealed that the correlation between employee performance and recruitment and selection were highly significant. In a study carried out by Amaram (2005) in the United States of America showed that headhunting recruitment strategy is the most effective channel of selection best and qualified candidates for vacant positions with high retention strategies. Similarly, Karemu et al. (2014) examined the factors influencing employee retention strategy. They found out that a significant relationship exists between employee e-recruitment, selection strategies, and employee retention. This implies that the presence of e-recruitment and selection practices would significantly lead to high employee retention. Mbugua et al. (2015: 87) on the relationship between strategic recruitment and employee retention showed that employee recruitment practices had a significant influence on employee retention through the use of associations, psychometric tests, website, targeting specific professionals and utilization of technologies. Shuku (2015:1) studied the effect of recruitment and selection practices on retention of teachers in international primary schools in Nairobi County.
The study made use of descriptive research design through the administration of structured questionnaires to 128 of 50 listed international primary schools in Nairobi County. The study also employs the Pearson Correlation and regression analysis in the analysis of data. It regression results showed that selection practice has a significant influence on the retention of teachers in international primary schools in Kenya. Midiwo et al. (2015) examined the influence of human resource information system on the performance of public Universities. They found out that e-recruitment strategy of candidate recruitment process had no significant effect on employee retention. Tsuma (2017) conducted empirical evidence on the influence of e-recruitment practices on employee retention in multinational corporations in Kenya. The study made use of descriptive survey research design through the distribution of questionnaires to the human resource managers of two-hundred and seventeen (217) multinational corporations based in Nairobi County.
The study employed descriptive statistics, correlation and multiple regression analysis in the analysis of data. The results from the multiple regression showed that e-recruitment strategy (corporate websites) had a significant influence on employee retention while e-recruitment strategy (commercial websites) had an insignificant influence on employee retention. Marwa (2018:20) carried out a study on strategic human resource management and public employee retention in National Bank of Egypt (NBE). The study used descriptive design and quantitative research in the collection of data. Selection practices had a significant impact on employee retention. Similarly, Wijesiri et al. (2019:2) studied the impact of human resource practices on employee retention. The study was conducted on the Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) sector in Sri Lanka. Primary data were collected through the distribution of a structured questionnaire to 237 executive level employees with the help of simple random sampling and analyzed through a deductive approach and simple regression technique. It would be revealed from the regression results that a selection practice of human resources has a weak significant impact on employee retention.
The theory that likened to the study under consideration is discussed subsequently.
The Resource-Based View (RBV) theory
The Resource-Based View (RBV) theory stresses that the attainment and retention of employees in a workplace with the sustainable competitive advantage is a function of resources and capabilities of the business organizations (Penrose, 1959). The resource-based view is a common theory of integration of social media to recruitment, online recruitment whether public or private sector organizations. This means that the use of e-recruitment as a networked model bring about the attraction and retention of employee (Girard and Fallery, 2013; Wanjiku, 2015; Mbugua et al., 2015). The study was anchored on the resource-based view theory because the theory is relevant in the area of recruitment and retention strategy of the employee since it demonstrates how a firm derives sustainable competitive advantage through the exploitation of the scarce characteristics of individuals who are talented. However, human resources provide the necessary human and intelligent assets for firms to compete within the markets they operate in and gain an advantage over other firms through acquiring and retaining such talent (Wernerfelt, 1984).
Expectancy theory
Expectancy theory thrives on the idea that people prefer certain outcomes from their behaviour to others by a given level of performance. An employee who desires promotion will only achieve high performance if he/she believe his/her behaviour will lead to a promotion or else he/she will not exert effort (Vroom, 1964). An employee may be unwillingly to work hard if that person believes his effort will not lead to task accomplishment or there are no rewards for performance or the employee does not value the rewards will enhance the employee to leave the organizations. Expectancy is the probability that the effort put forth will lead to the desired performance. When the probability of some effort will not be rewarded, the employee will not be highly motivated to perform a certain task and bring about a high level of employee turnover (Vroom, 1964).
Research design
The study used a descriptive survey research design. Zikmund (2003) is of the view that surveys provide a quick and accurate means of accessing information on a population at a single point in time. Collins and Hussey (2003:66) see descriptive survey research design as a technique used to gather statistical information about attributes, attitudes or actions of a population by administering standardized questions to some, or all of its respondents. Moreover, descriptive surveys can be conducted with personal interviews, postal and self-administered questionnaires. The target population for this study was made up of employees of Zenith bank Plc operating as a money deposits bank in Egor local government area, Oredo local government area, and Ikpoba- Okha local government area in the Benin City of Edo State. Therefore, the population size for Zenith Bank in Benin City was approximately 220. The sample size of this study was calculated using the Yamane (1967) statistical formula which would be applied as (Yamane, 1967):
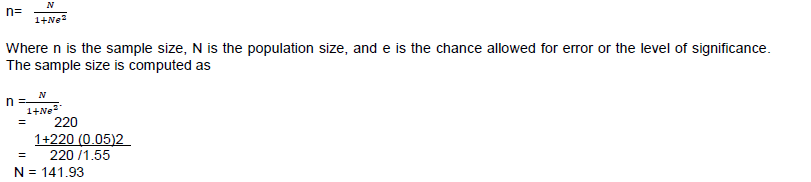
This value was approximated to the nearest round figure of 140. Consequently, a sample size of 140 was used.
Model specification and measurement of variables
Therefore, the model specification with an error term is stated below:
EMPR = α + β1 HDH+ β2SPR+ εt
Where: EMPR = Employee retention strategy; HDH = Headhunting recruitment strategy; SPR = Selection practices; α = intercept and ε = Errors
The explanatory variables were measured by a research instrument. Therefore, the questionnaire instrument would be constructed using a five-point Likert scale (5 for strongly agreed to 1 for strongly disagreed). The reliability of the questionnaire was tested using Cronbach’s Alpha. Tavakol and Dennick (2011) posit that reliability is the ability of an instrument to measure consistently. Reliability of an instrument is closely associated with its validity. The general agreed lower and acceptable limit for the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient is 0.70. The reliability test conducted with help of the Cronbach’s alpha showed that employee retention strategy has an internal consistency of 0.723, headhunting recruitment has an internal consistency of 0.784 and selection practice has an internal consistency of 0.786. This showed that the Cronbach’s Alpha for the dependent variable and independent variables were more than 0.70. The variables were considered to be good for the measurement of internal consistency which is between 0 and 1.
Estimation technique
Multivariate regression technique was adopted to test the significant effect of the given variables for the study with the help of Stata 13.0 econometric software and Alpha test performed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS), version 21.0.
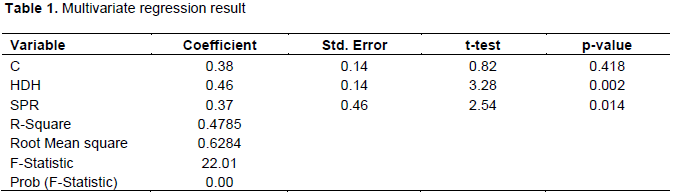
A total of one-hundred and forty (140) questionnaires were given out to respondents and one-hundred and ten (110) questionnaires were duly returned and usable, and subsequently analyzed. The response rate was about 79%. In order to test the individual significance of the variables, the multivariate regression technique was adopted and the result is presented in Table 1. As shown in the table, the coefficient of determination (R2) value of 0.0.4785 that is about 48% of the systematic variations in the dependent was jointly explained by independent variables. The root mean square of 0.6284 means that the model overall is good for statistical prediction at about 63%. The F-statistic value of 22.01 and its associated value of 0.00 revealed that there was a significant linear relationship between the variables. The empirical result showed that headhunting recruitment strategy (HDH) has a significant positive effect on employee retention strategy at 1% level of significance. This means that headhunting recruitment strategy adopted by money deposit in bank would significantly lead to a high level of employee retention. The significant effect of headhunting recruitment strategy was because the variable has a p-value < 0.05. The result was consistent with the findings of Amaram (2005) that headhunting recruitment strategy is the most effective channel of selection for best and qualified candidates for vacant positions with high retention strategies. The study, therefore, suggested that the hypothesis that headhunting recruitment strategy has no significant effect on employee retention strategy should be rejected. The result also revealed that selection practices (SPR) have a significant positive effect on employee retention strategy at 1% level of significance. This implies that selection practice employed by money deposit banks bring about the level of employee retention. The significant effect of selection practices was because the variable has a p-value < 0.05. The result was consistent with the findings of Mbugua et al. (2015) and Shuku (2015) that selection practice has a significant influence on employee retention strategy. The study of Wijesiri et al. (2019) also supported the results that selection practice of human resources has a weak significant impact on employee retention. The study of Marwa (2018) also affirmed that results selection practices had a significant impact on employee retention. The study, therefore, suggested that the hypothesis should be rejected that selection practice has no significant effect on employee retention strategy.
Employee retention is seen as one of the most deliberated concepts in the area of human resource management and putting proactive strategy and implementing the necessary policies to retain employees in a competitive market environment. The recruitment and selection process is one of the most important human resource management used by banks. Headhunting is a human resource management strategy employed by the management of the banking industry for the process of recruitment and selection of appropriate candidates for various vacant positions. Headhunting is a recruitment and selection process where the recruiters find the contact details of a specific candidate that has some specific skills so as to participate in the recruitment process. Headhunting is an external recruitment policy whereby outsourcing organizations have to suitable candidates employed elsewhere to fill the business position. In other words, employee retention is a practice needed to be adopted in the corporate organization in order to encourage employees to remain for as specified in the contracts agreement. The results showed that headhunting recruitment strategy has a significant positive effect on employee retention strategy at 1% level of significance and selection practice has a significant positive effect on employee retention strategy at 1% level of significance. Based on the above empirical findings and conclusions, the following recommendations are put forward. Firstly, headhunting recruitment strategy and selection practices should be embraced by human resource managers in the banking industry because it is keen on employee retention. Secondly, the management of the banking industry should see selection practice as a human resource recruitment policy that brings about higher employee retention. Thirdly, policies on employee recognition and promotion should be adopted by human resource managers of bank with respect to hard work, honesty, and integrity for a higher level of employee retention. Fourthly, the study suggested that further empirical study should be carried out on the areas of headhunting recruitment and employee retention by extending the scope to other non- financial quoted companies in Nigeria.
Some of the limitations of the study are limited sample size and poor responses from the sampled respondents: The sample size of the study was limited due to exclusion of customers and employees from other money deposit banks. Also, the use of research instrument (questionnaire) is usually prone to the unwillingness of the respondents to objectivity fill and answers the questions as a result of a busy schedule.
The authors have not declared any conflict of interests.
REFERENCES
|
Al-Qudah MKM, Osman A, Ab Halim MS, Al-Shatanawi HA (2014). The effect of human resources planning and training and development on organizational performance in the government sector in Jordan. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences 4(4):79.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
Akala HS (2012). Factors influencing employee retention among the non-teaching staff at the University of Nairobi, Kenya. The University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya. Available at:
View
|
|
|
|
|
Akintayo DI (2010). Work-family role conflict and organizational commitment among industrial workers in Nigeria. Journal of Psychology Review 2(1):1-8.
|
|
|
|
|
Amaram DI (2005). Issues in recruitment and retention for the IT workforce. Journal of American Academy of Business 6(2):49-54.
|
|
|
|
|
Beardwell J, Wright M (2012). Recruitment and selection. In Beardwell, Human resource management: A contemporary approach. Harlow: Pearson Education Limited. pp. 189-229.
|
|
|
|
|
Cropanzano R, Byrne ZS, Bobocel, DR, Rupp DR (2001). Moral virtues, fairness heuristics, social entities, and other denizens of organizational justice. Journal of Vocational Behaviour 58:164-209.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Collins J, Hussey R (2003). Business research. Basingstoke NH.
|
|
|
|
|
Das B, Baruah M (2013). Employee retention: A review of the literature. IOSR Journal of Business and Management 14(2):8-16.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Deepakshi G, Sheetal C (2014). Social Networking Sites.A new recruitment tool for human resource. The International Journal of Business and Management 2(4):2-3.
|
|
|
|
|
Dessler G (2007). Basics of human resource management.
|
|
|
|
|
Dessler G (2014a). Pearson New International Edition Fundamentals of Human Resource Management.
|
|
|
|
|
Dessler G (2014b). Fundamentals of Human Resource Management: Pearson New International Edition. Pearson Education Limited.
|
|
|
|
|
De Waal A, Frijns M (2011). Longitudinal research into factors of high performance: the follow-up case of Nabil Bank. Measuring Business Excellence 15(1):4-19.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Eisenberger R, Stinglhamber F, Vandenberghe C, Sucharski IL, Rhoades L (2002). Perceived supervisor support: Contributions to perceived organizational support and employee retention. Journal of Applied Psychology 87(3):565.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Gazzawi K, Accoumeh A (2014). Critical success factors of the e-recruitment system. Journal of Human Resources Management and Labor Studies 2(2):159-170. Available at:
View
|
|
|
|
|
Girard A, Fallery B (2009). E-recruitment: new practices, new issues. An exploratory study. Available at:
View
|
|
|
|
|
Imran R, Majeed M, Ayub A (2015). Impact of organizational justice, job security, and job satisfaction on organizational productivity. Journal of Economics, Business, and Management 3(9):840-844. Available at:
View
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
James L, Mathew L (2012). Employee Retention Strategies: IT Industry. SCMS Journal of Indian Management 9(3):79-87.
|
|
|
|
|
Karemu G, Kahara G, Josee V (2014). An analysis of the effect of employee recruitment strategies on employee retention at Equity Bank, Kenya. European Journal of Business and Management 6(17):90-97.
|
|
|
|
|
Marwa GAF (2018). Strategic human resource management and public employee retention. Review of Economics and Political Science 3(2):20-39.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Mbugua G, Waiganjo E, Njeru A (2015). Relationship between strategic recruitment and employee retention. International Journal of Business Administration 6(1):87-97.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Midiwo J, Mukulu E, Gichuhi W (2015). Influence of HRIS on the performance of Public Universities. International Journal of Human Resource and Procurement 1(3):295-317.
|
|
|
|
|
Newell S (2005). Recruitment and selection. Managing human resources: Personnel management in transition. pp. 115-147.
|
|
|
|
|
Ombui K, Mukulu E, Waititu GA (2012). The influence of recruitment and selection on the performance of employees in research institutes in Kenya. International Journal of Science and Research 2(3):19-64.
|
|
|
|
|
Rathling S (2012). The recruiter's lounge research advisory panel (2006) e-recruitment practices and trends in Ireland, Public Appointments Service.
|
|
|
|
|
Samuel M, Chipunza C (2009). Employee retention and turnover: Using motivational variables as a panacea. African Journal of Business Management 3(8):410-415.
|
|
|
|
|
Shuku R (2015). Effect of recruitment and selection practices on the retention of teachers in international primary schools in Nairobi County. A Research Project Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Award of Master of Business Administration, School of Business, University of Nairobi pp. 1-66.
|
|
|
|
|
Smith A, Rupp W (2004). Managerial challenges of e-recruiting: extending the life cycle of new economy employees. Online Information Review 28(1):61-74.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Sinha V, Thaly P (2013). A review on changing trend of recruitment practice to enhance the quality of hiring in global organizations. Journal of Contemporary Management Issues 18(2):141-156.
|
|
|
|
|
Subramaniam C, Shamsudin FM, Ibrahim H (2011). Linking human resource practices and organizational performance: Evidence from small and medium organizations in Malaysia. Journal Pengurusan 32:27-37.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Suvankulov F, Lau MCK, Chau FHC (2012). Job search on the internet and its outcome. Emerald Internet Research 22(3):298-317.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Tavakol M, Dennick R (2011). Making sense of Cronbach's alpha. International Journal of Medical Education 2:53.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Trivedi J, Muduli A (2015). Research on recruitment outcomes and recruitment methods under the mediating impact of credibility & satisfaction. International Journal of Advancement in Engineering, Technology, Management and Applied Science 2(9):26-53.
|
|
|
|
|
Tsuma P (2017). Influence of e-recruitment practices on employee retention in multinational corporations in Nairobi County (Thesis). Strathmore University. Available at:
View
|
|
|
|
|
Valkonen J, Huilaja H, Koikkalainen S (2013). Looking for the right kind of person: recruitment in nature tourism guiding. Scandinavian Journal of Hospitality and Tourism 13(3):228-241.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Vroom VH (1964). Work and motivation (Vol. 54). New York: Wiley.
|
|
|
|
|
Walker AJ (2001). How the web and other key trends are changing human resources, in Alfred Walker, ed. Web-based human resources, New York: McGraw-Hill.
|
|
|
|
|
Wanjiku KR (2015). Perceived effectiveness of E-Recruitment in talent acquisition in the Kenyan Public Service. Available at:
View
|
|
|
|
|
Wernerfelt B (1984). A resourceâ€based view of the firm. Strategic Management Journal 5(2):171-180.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Wijesiri NRASS, Paranagama GS, Sirirwardhana MMAS, Thilakarathna DLNC, Weerarathna RS, Pathirana UPGY (2019). The impact of human resource practices on employee retention: A Case of BPO Sector, Sri Lanka. International Journal of Human Resource Studies 9(1):1-21.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Yamane T (1967). Statistics: an introductory analysis Harper and row. New York, Evanston and London and John Weather Hill. Inc., Tokyo.
|
|
|
|
|
Zhou J, Qian X, Henan Q, Lei X (2009). Total reward strategy: A human resources management strategy going with the trend of the times. International Journal of Business and Management 4(11):177-182.
Crossref
|
|
|
|
|
Zikmund WG (2003). Exploring marketing research (7th edition). USA: Thomson, South Western.
|
|